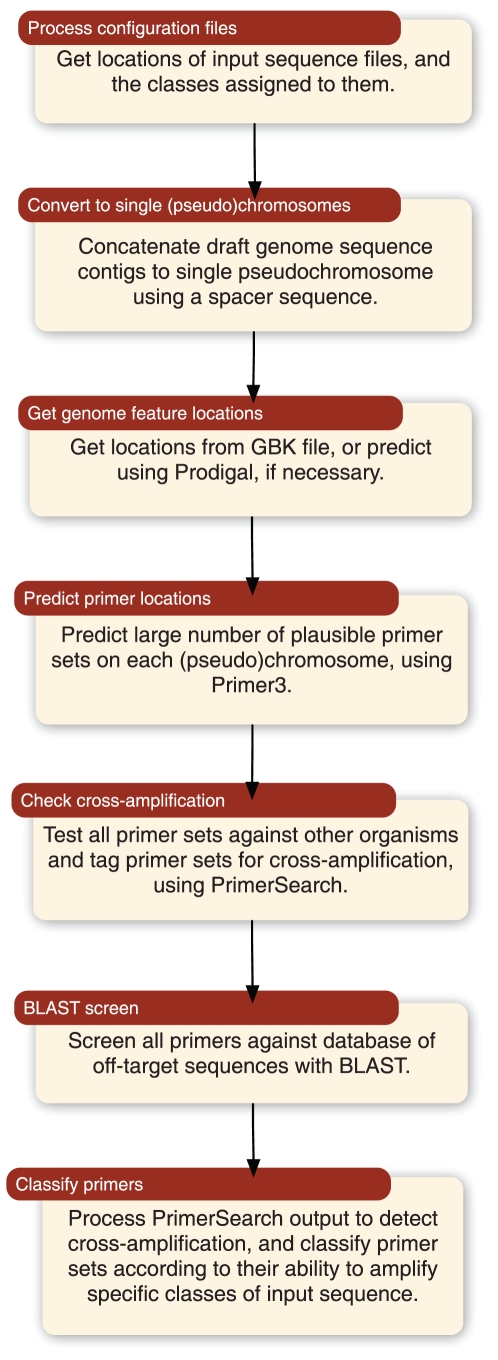
Figure 2. Flowchart of the primer design process.
The locations of input training set sequence files, and their classifications, are read from a configuration file. Input sequences comprising several smaller sequences (e.g. contigs of a draft genome) are concatenated using a spacer sequence. Locations of coding sequences (CDS) are obtained from a GenBank file if available, or predicted using a genecaller. A large number (>1000) of primers is then designed to each input sequence. Primers that lie within CDS are tested in silico for their ability to cross-amplify other members of the training set, and compared against a larger set of off-target sequences to discard non-specific primers. The surviving primers are classified according to their ability to amplify specific classes of sequence from the training set. A more detailed flowchart of the pipeline is given in Supplementary Figure S1.