Figure 1.
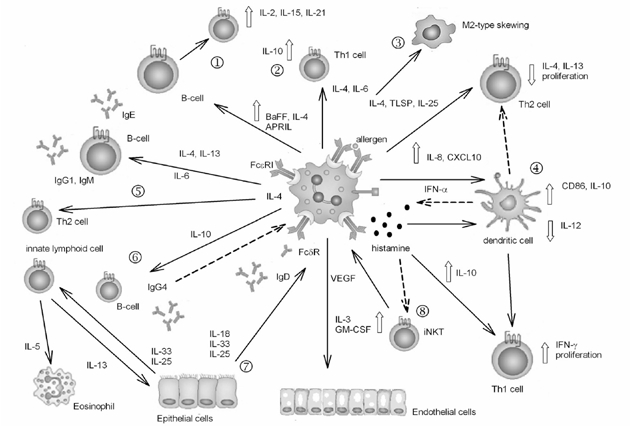
Cartoon illustrating the effector functions and immune regulatory actions involving basophils. Dashed lines show inhibitory and feedback pathways. ➀Basophil participation in B-cell survival, maturity and apoptosis: IgD, binding to basophils, contribute to immuno-regulation towards B cells (by IL-4, B➀AFF and APRIL) and towards dendritic cells in which it up-regulates IL-8 and CCL10 production. ➁IL-6 induction of IL-10 by Th1 cells: basophil regulates the role of dendritic cells in balancing Th1/Th2 responses, participates in the skewing of IFN-γ producing Th1 to IL-10-producing cells, regulates basophil activation by IFN-α and inhibits IL-3 and GM-CSF producing iNKT. ➂Macrophage type 2 skewing; ➃Participation in dendritic cells' regulation of Th2/Th1 balance; ➄Activation of Th2 and B-cell humoral response: the role of basophil is central in inducing Th2 differentiation, B-cell production of IgE and of B-cell memory and regulates allergy by inducing IL-10 production and IgG4; ➅Down-regulation of allergic inflammation by IgG4 and IL-10; ➆Inflammatory response mediated by IL-18, IL-25 and IL-33: the basophil is linked to tissue function by producing VEGF and by responding to several factors, such as IL-18, IL-25 and IL-33, which in turn promote IL-5 production by Th2-cells able to recruit eosinophils. ➇Production of histamine as an effector molecule and immune modulator. For further information see the text.
