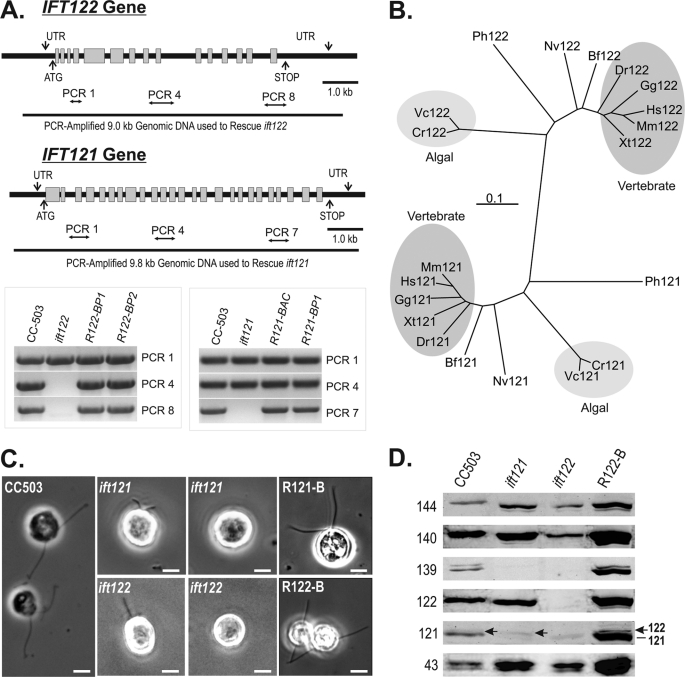
FIGURE 5.
The loss of Chlamydomonas IFT121 or IFT122 results in distinctive disruptions to IFT complex A, both of which severely disrupt ciliogenesis. A, genomic maps and PCR analysis of genomic DNA isolated from wild-type, mutant, and rescued strains. R122-BP1, R122-BP2, and R121-BP1 represent mutant strains that were rescued with PCR-amplified genomic DNA, whereas R121-BAC represents an ift121 mutant strain that was rescued using intact BAC DNA. B, taxonomic relatedness of the IFT122 and IFT121 gene products. Cr, C. reinhardtii; Vc, Volvox carteri; Hs, Homo sapiens; Mm, Mus musculus; Gg, Gallus gallus; Xt, Xenopus tropicalis; Dr, Danio rerio; Bf, Branchiostoma floridae; Nv, Nematostella vectensis; Ph, Pediculus humanus corporis. C, phase-contrast images of ift121 and ift122 strains reveal cells with short or no flagella; >95% of ift121 and ift122 rescued with isolated BAC DNA containing IFT121 or IFT122 or PCR-amplified genomic fragments of the IFT121 and IFT122 genes, respectively, recovered assembly of full-length flagella. D, the levels of IFT A proteins extracted from 2 × 106 cells are measured using immunoblots. Soluble protein extracts from whole Chlamydomonas cells were resolved by SDS-PAGE on 10% polyacrylamide gels and transferred to nitrocellulose membrane before probing with antibodies against each of the six IFT A proteins. R122-B represents an ift122 mutant strain in which flagellar assembly was rescued using intact BAC DNA; R121-B represents an ift121 mutant strain rescued using PCR-amplified genomic IFT121.