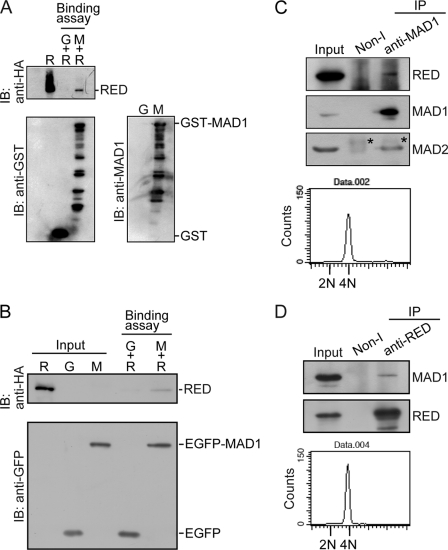
FIGURE 2.
MAD1 binds to RED. A and B, MAD1 binds to RED in vitro. A, purified GST-MAD1 interacts with His-HA-RED. Purified GST (G) or GST-MAD1 (M) recombinant fusion proteins were incubated with purified His-HA-RED (R) recombinant proteins in RIPA buffer and precipitated with glutathione-Sepharose beads at 4 °C. The precipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblot (IB). Purified His-HA-RED (R) recombinant protein was loaded as an input control. B, affinity-purified EGFP-MAD1 interacted with His-HA-RED. Affinity-purified EGFP (G) or EGFP-MAD1 (M) fusion proteins were incubated with purified His-HA-RED recombinant proteins (see “Experimental Procedures”). The precipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblot. Purified EGFP, EGFP-MAD1, and His-HA-RED recombinant proteins were loaded as input controls. C and D, MAD1 binds to RED in vivo. Nocodazole-arrested mitotic cells were shaken off and released from arrest in fresh medium lacking nocodazole for ∼40 min. Mitotic cells were collected again for coimmunoprecipitation assays and DNA content analysis by flow cytometry. About 2 mg of cell lysates were used for immunoprecipitation (IP) assay. Immunoprecipitated proteins were determined by immunoblot. C, RED was coimmunoprecipitated with the purified rabbit anti-MAD1 antibodies using protein G beads from mitotic cell lysates. The purified rabbit non-immune (non-I) antibody was used as a control. Eighty micrograms of cell lysates were loaded as an input control. The asterisks indicate the light chain of rabbit IgG. D, MAD1 was coimmunoprecipitated with the purified rabbit anti-RED antibodies using protein G beads from mitotic cell lysates. 45 μg of cell lysates was loaded as an input control.