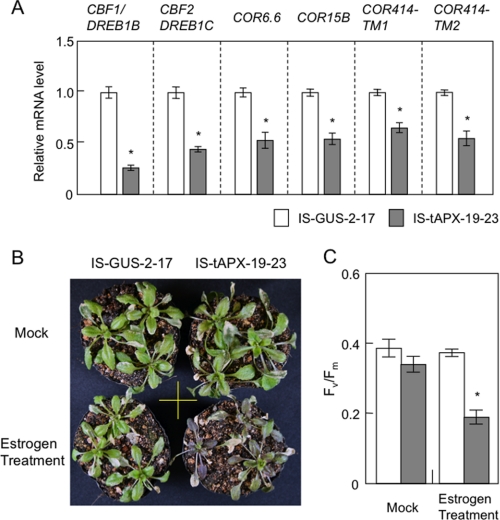
FIGURE 5.
Effect of tAPX silencing on cold acclimation. A, 17-day-old IS-GUS-2-17 and IS-tAPX-19-23 plants were sprayed with a 100 μm estrogen and kept under NL. At 48 h after the estrogen treatment, the transcript levels of RTS genes (CBF1/DREB1B, CBF2/DREB1C, COR6.6, COR15B, COR414-TM1, and COR414-TM2), known to be involved in cold acclimation, were measured by q-PCR. Error bars indicate S.D. (n = 3). Significant differences: *, p < 0.05 versus the value for IS-GUS-2-17 plants. B and C, 17-day-old IS-GUS-2-17 and IS-tAPX-19-23 plants were sprayed with a 100 μm estrogen solution or water (Mock) and transferred to cold stress conditions (100 μmol photons m−2 s−1, 4 °C) for 2 weeks. The treatment with estrogen was performed every 3 days to maintain the tAPX silencing. B, 14 days after cold stress, the IS-GUS-2-17 and IS-tAPX-19-23 plants were photographed. The same results were obtained in four independent experiments. C, Fv/Fm values in the leaves of IS-GUS-2-17 and IS-tAPX-19-23 10 days after cold stress were measured using a Closed FluorCam 800MF. Error bars indicate S.D. (n = 3). Significant differences: *, p < 0.05 versus the value of IS-GUS-2-17 plants.