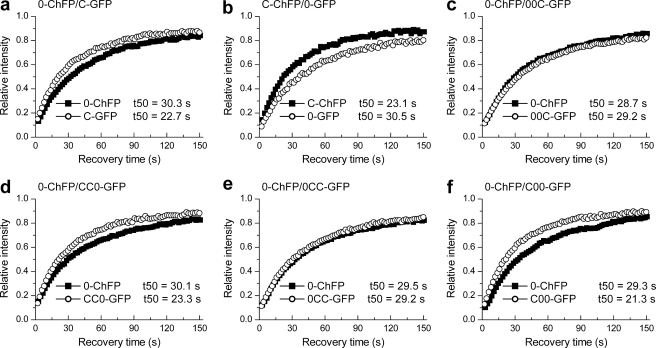
FIGURE 3.
Quantitative analysis of the relative binding kinetics of isotypes H10 and H1c and effects of swapping their terminal domains. a and b, FRAP analysis with cells co-expressing WT H10-ChFP and WT H1c-GFP (a) or WT H10-GFP and WT H1c-ChFP (b) shows faster recovery kinetics for H1c than H10. c–f, simultaneous recovery curves of the C-terminal switch mutants 00C-GFP relative to WT H10-ChFP (c) and CC0-GFP relative to WT H10-ChFP (d) and of the N-terminal switch mutants 0CC-GFP relative to WT H10-ChFP (e) and C00-GFP relative to WT H10-ChFP (f). The values for the half-time of recovery (t50) were determined as previously described (35) and represent the means ± S.D. of at least eight independent measurements from a pool of three stable cell lines. The error bars are omitted from the plots for clarity. Table 2 provides the corresponding statistical analyses.