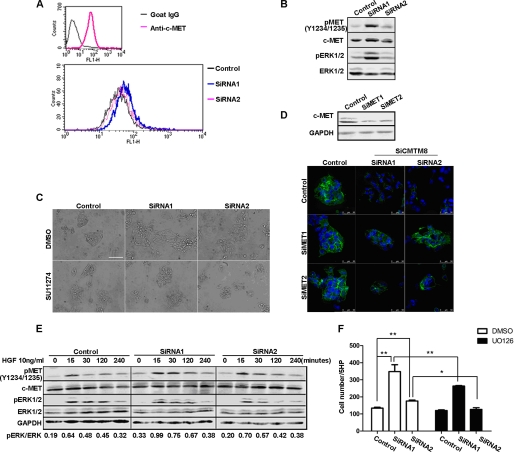
FIGURE 4.
HGF/c-MET signaling is activated and required for EMT-like phenotypic alterations in HepG2 cells with CMTM8 knockdown. A, flow cytometric analysis of c-MET on the surface of HepG2 cells transfected with non-silencing RNA or siRNAs for CMTM8 knockdown. B, immunoblot of cell lysates from HepG2 cells transfected with control or CMTM8 siRNAs. C, phase-contrast images showing the morphology of HepG2 cells transfected with non-silencing siRNA or siRNAs for CMTM8 knockdown and treated with Me2SO or SU11274 (5 μm). Scale bar = 100 μm. D, confocal images of indirect immunofluorescence of HepG2 cells cotransfected with control or CMTM8 siRNAs (SiCMTM8) and control or c-MET siRNAs (SiMET) and stained with anti-E-cadherin antibody. Scale bars = 50 μm. The immunoblot of c-MET shows the knockdown efficiency of c-MET siRNAs in HepG2 cells. E, immunoblot of cell lysates from HepG2 cells transfected with control or CMTM8 siRNAs, serum-starved, and stimulated with 10 ng/ml HGF for the indicated times. F, migration assay. 1 ng/ml HGF was used as the chemoattractant for HepG2 cells transfected with control or CMTM8 siRNAs and pretreated with Me2SO or U0126 (10 μm) for 2 h. Error bars indicate S.E. (n = 3). **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05 (two-tailed unpaired t test). 5HP indicates five high-powered fields of view.