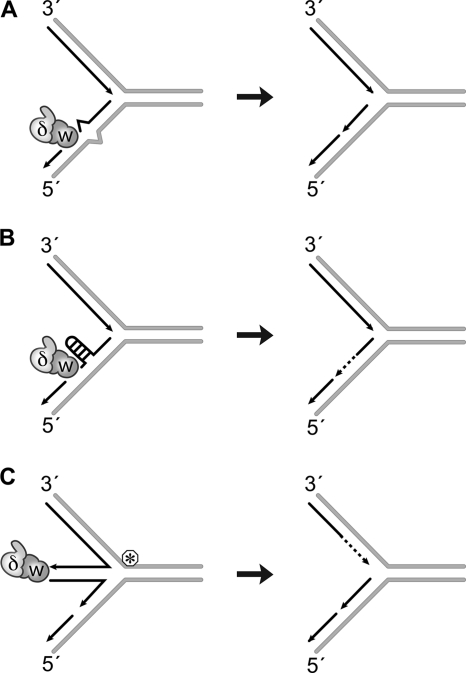
FIGURE 10.
Model for WRN and Pol δ exonuclease function at replication forks. Hydrolysis of a single mismatched nucleotide at the 3′-primer terminus (A) or that of alternate DNA structures assumed by the newly synthesized strand (B) could facilitate uninterrupted DNA synthesis by DNA Pol δ on the lagging strand. Alternately, replication forks stalled by a lesion/roadblock are believed to form four-stranded structures. Hydrolysis of DNA in such structures could ensure accurate synthesis after lesion repair (C). W, WRN; δ, Pol δ; circled asterisk, lesion/replication roadblock.