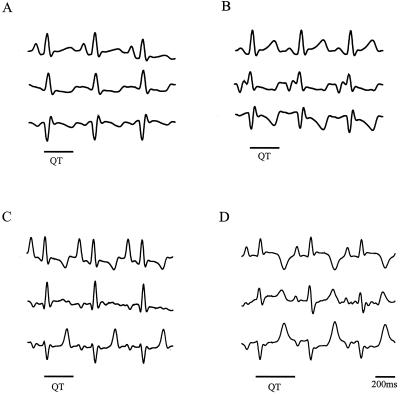
Figure 4.
The LQTS mutant KCNE1-D76N prolongs the QT interval in guinea pigs in vivo, whereas HERG-G628S does not affect QT interval duration. ECG recordings were performed after widespread myocardial infection with HERG-G628S or KCNE1-D76N. ECGs revealed a prolongation by ≈23% of QTc 48 h after KCNE1-D76N infection (D) compared with immediate postoperative recordings (C) (QTc 286.7 ± 10.4 ms vs. 353.3 ± 24.5 ms, n = 3; P = 0.04), consistent with the marked prolongation of action potentials in KCNE1-D76N-infected ventriculocytes. Conversely, no change in QTc was observed 48 h after infection with HERG-G628S (B) compared with immediate postoperative ECGs (A) (305.0 ± 11.4 ms vs. 293.0 ± 9.5 ms, n = 3; P = 0.38), in agreement with the overall unchanged APD of HERG-G628S-infected cells.