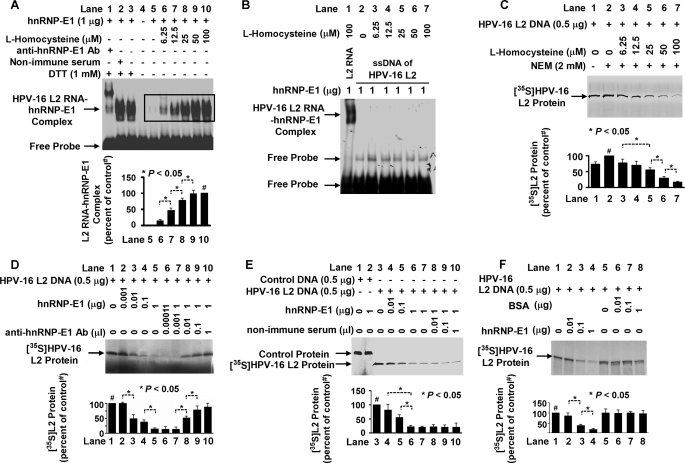
FIGURE 1.
Characterization of RNA-protein interactions involving purified recombinant GST-hnRNP-E1 protein and HPV16 L2 RNA cis-element in the presence of increasing concentrations of l-homocysteine, leading to the translation of HPV16 L2 protein in vitro. A, gel shift analysis of the interaction of HPV16 L2 RNA cis-element (1 × 105 cpm) and GST-hnRNP-E1 protein in the absence or presence of various concentrations of l-homocysteine and the influence of nonimmune or anti-hnRNP-E1 antiserum on RNA-protein complex formation using 6% native PAGE and autoradiography. The pooled densitometric scanned data of RNA-protein complexes formed with increasing concentrations of l-homocysteine from three independent gel shift experiments are shown as a bar graph below one representative gel; these data are presented as the mean ± S.D. (error bars). The scanned area reflecting the L2 RNA-hnRNP-E1 protein signals formed with increasing concentrations of l-homocysteine is marked by a rectangle in the gel from lanes 5–10 and compared with the signal formed in the presence of 100 μm l-homocysteine in lane 10 (# signifies the 100% value). B, interaction between the single-stranded sense DNA (ssDNA) of HPV16 L2 and homocysteinylated hnRNP-E1. Lane 1 contains a positive control using HPV16 L2 RNA. C–F, in vitro translation of [35S]HPV16 L2 protein under various experimental conditions. In each of the following panels, the pooled densitometric scanned data of [35S]HPV16 L2 protein synthesized from three independent experiments are shown as a bar graph below one representative gel; these data are presented as the mean ± S.D. # in C, D, E, and F signifies the 100% value. C, effect of the addition of physiological concentrations of l-homocysteine on the biosynthesis of HPV16 L2 protein during in vitro translation. NEM, N-ethyl maleimide. D, effect of the addition of purified recombinant GST-hnRNP-E1 during in vitro biosynthesis of HPV16 L2 (lanes 2–5) and effect of increasing concentrations of anti-hnRNP-E1 antiserum (anti-hnRNP-E1 Ab) in quenching the inhibitory effect of GST-hnRNP-E1 on HPV16 L2. E, effect of increasing concentrations of nonimmune serum on the translation of HPV16 L2 in the presence of purified recombinant GST-hnNP-E1. F, comparison of the effect of the addition of purified recombinant GST-hnRNP-E1 versus BSA on HPV16 L2 protein synthesis.