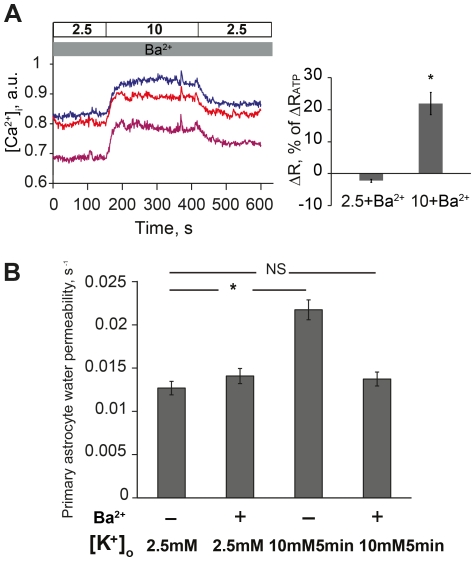
Figure 4. Functional relationship between Kir-channels and potassium effect on astrocyte water permeability.
(A) Left panel shows representative recordings of intracellular calcium ([Ca2+]i) in three individual primary astrocytes loaded with Fura-2 AM during perfusion with indicated concentrations of potassium (mM) and 100µM barium (Ba2+). With barium, 10mM potassium triggered a global [Ca2+]i increase (∼150–420s). Right panel shows summarized calcium data normalized to the peak [Ca2+]i induced by ATP, n = 147. (B) The astrocyte water permeability increase caused by 10mM potassium was abolished when cells were preincubated with 100µM barium (*p<0.001). There was no difference in water permeability in control cells exposed to basal potassium concentrations with or without preincubation with barium (2.5mM potassium -/+ 100µM barium, p = 0.24), n = 60–89.