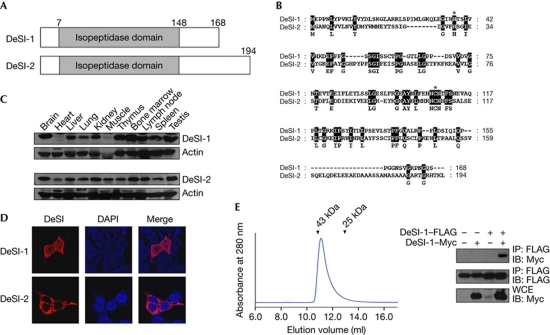
Figure 1.
Identification of DeSI. (A) Schematic representation of the structure of DeSI-1 and DeSI-2. (B) Sequence alignment of DeSI-1 and DeSI-2. Amino acid identity is highlighted in black. The histidine and cysteine residues that form the catalytic site of cysteine protease are marked by asterisks. (C) Tissue expression pattern of DeSI-1 and DeSI-2. Murine tissue lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using rabbit anti-DeSI-1 or anti-DeSI-2 antibodies. Equal protein loading was shown by immunoblotting with anti-actin antibody. (D) Subcellular localization of DeSI-1 and DeSI-2. 293T cells were transfected with expression plasmids encoding Myc-tagged DeSI-1 or DeSI-2. Cells were visualized by staining with anti-Myc antibody along with Alexa 568-conjugated secondary antibody (red). (E) Homodimerization of DeSI-1 (left panel). The chromatogram shows that full-length DeSI-1 (Mr=20 kDa) was eluted as a ∼40-kDa protein from a Superdex 75 column. The arrowheads indicate the elution positions of the size marker proteins (right panel); 293T cells were transfected with the indicated combinations of expression plasmids encoding DeSI-1–FLAG and DeSI-1–Myc. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with the anti-FLAG antibody and subsequently to immunoblot analysis with anti-Myc or anti-FLAG antibodies. DAPI, 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; DeSI-1, DeSumoylating Isopeptidase 1; IB, immunoblot; WCE, whole-cell extract.