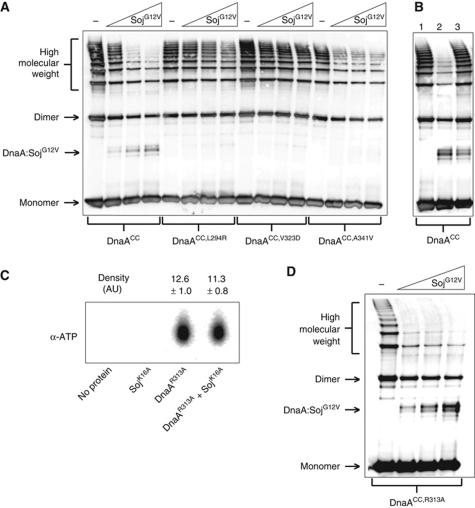
Figure 5.
Monomeric Soj specifically prevents DnaA oligomerization in vitro. (A) In vitro oligomer formation assay with DnaASup proteins. DnaA proteins (3 μM) and SojG12V (12, 24, and 36 μM) were incubated in oligomer formation buffer in the presence of ATP (2 mM) and DNA (pBsoriC4; 3 nM) for 15 min prior to the addition of BMOE. DnaA proteins were separated by SDS–PAGE and visualized by western blotting. (B) Monomeric Soj is unable to disassemble pre-formed DnaA oligmers. Reaction conditions are the same as in (A). DnaA was crosslinked at T=15 min. Lane 1, DnaA was added to the reaction buffer at T=13. Lane 2, SojG12V was added at T=0 and DnaA added at T=13. Lane 3, DnaA was added at T=0 and SojG12V added at T=13. (C) Monomeric Soj does not affect DnaA ATP binding. DnaAR313A (3 μM) and/or SojK16A (36 μM) were incubated with α-P32 ATP before being isolated from the reaction using magnetic nickel beads and denatured with methanol. The released nucleotides were separated on a PEI cellulose TLC plate and visualized by autoradiography. Density values were measured using ImageJ (n=3). (D) Monomeric Soj disrupts DnaA oligomers independent of DnaA ATPase activity. In vitro oligomer formation assay with the ATP hydrolysis deficient DnaA protein. DnaAR313A (3 μM) and SojG12V (12, 24, and 36 μM) were incubated in oligomer formation buffer in the presence of ATP (2 mM) and DNA (pBsoriC4; 3 nM) for 15 min prior to the addition of BMOE. DnaA proteins were separated by SDS–PAGE and visualized by western blotting.