Figure 1.
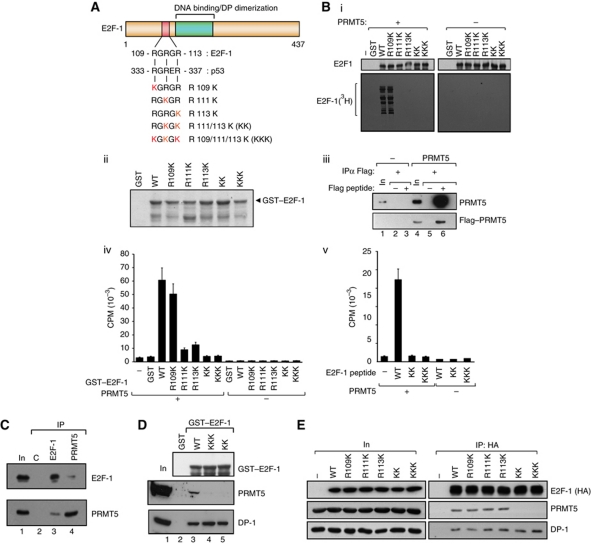
E2F-1 undergoes arginine methylation by PRMT5. (A) Location of the RGRGR sequence motif in E2F-1, highlighting its similarity with the region in p53 targeted by PRMT5 (Jansson et al, 2008). The arginine (R) residues mutated to lysines (K) in the E2F-1 mutants are indicated (in red), together with the designation of the different mutant derivatives. (B) Each of the indicated GST–E2F-1 proteins (about 1 μg; ii) was used in the methylation reaction (i). In vitro methylated samples were analysed by SDS–PAGE as described. Quantitation of either GST–E2F-1 (iv) and associated mutant derivatives (A) or a 20-residue peptide (from residue 100 to 120) together with the equivalent KK and KKK peptides (v) after in vitro methylation by PRMT5. Incorporation of 3H-methyl groups was measured as DPM. Coomassie stain of the GST–E2F-1 proteins is shown in (ii), and the Flag–PRMT5 immunoprecipitated from transfected cells in (iii), which was used in (i, iv, v). (C) Endogenous E2F-1 or PRMT5 was immunoprecipitated with either anti-E2F-1 or anti-PRMT5 from untransfected U2OS cells and subsequently immunoblotted with anti-PRMT5 or anti-E2F-1 as indicated. The input (In) and control (C) immunoprecipitations (IPs) are indicated. (D) Binding of E2F-1 to PRMT5. The indicated GST–E2F-1 proteins were incubated with U2OS cell lysate, and bound proteins immunoblotted using anti-DP-1 or PRMT5 antibodies. The level of GST–E2F-1 input protein (top anti-GST immunoblot) is indicated. (E) Either WT E2F-1 or the indicated mutant derivative expression vectors were transfected into U2OS cells and HA11 antibody was used for IP followed by immunoblotting with HA11 (E2F-1), PRMT5 or DP-1 as indicated. The level of ectopic E2F-1 input (In) protein is shown, and (−) indicates empty vector control transfected cells. Figure source data can be found with the Supplementary data