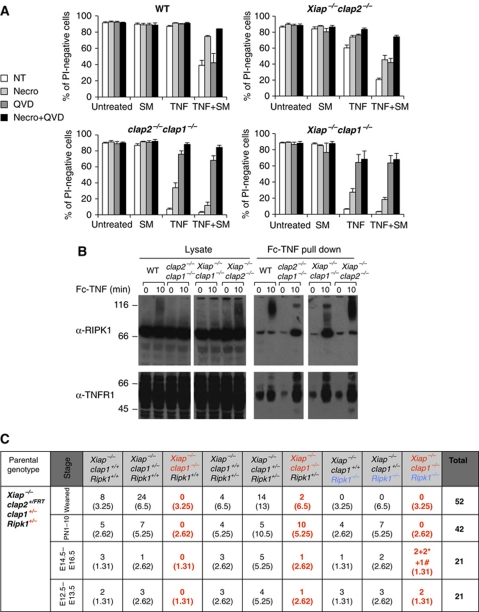
Figure 6.
In the absence of IAPs, both TNF-induced death of MEFs, and embryonic death during development, involves RIPK1. (A) Together, the RIPK1 kinase inhibitor necrostatin and the caspase inhibitor QVD protect IAP gene deleted MEFs from killing by TNF. MEFs derived from WT and compound mutant embryos were incubated for 24 h with or without 100 ng/ml Fc-TNF and 500 nM SM in the presence or absence of 50 μM necrostatin or 10 μM QVD. Cells were stained with PI and analysed by flow cytometry. The mean values+s.e.m. of 3–11 independent experiments are shown. (B) TNF-induced RIPK1 modification fails, and receptor-associated RIPK1 is increased when cIap1 genes are deleted. MEFs were stimulated with 1 μg/ml Fc-TNF prior to Fc pull down, and analysed by western blotting. (C) Incidence genotypes of offspring from Xiap−/−cIap1+/−Ripk1+/− intercrosses. *Represents embryos without heartbeat or reabsorbed and # represents embryos alive but with a small liver. See also Supplementary Figure S3. Figure source data can be found in Supplementary data.