Figure 2.
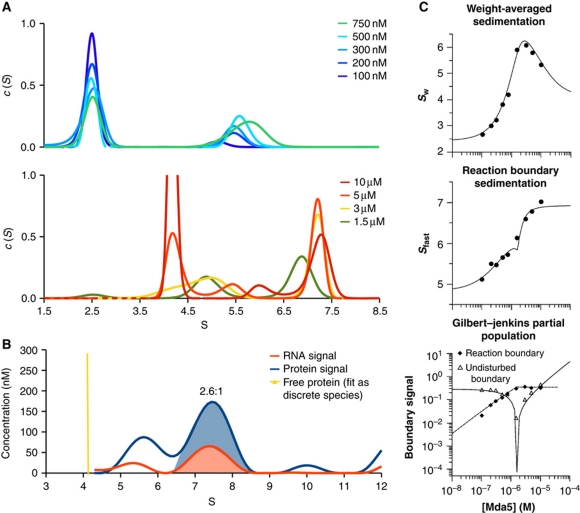
Short dsRNA induces rapid and cooperative dimerization of CARD-deleted MDA5. (A) The sedimentation coefficient distributions, c(S), calculated from SV-AUC with 1 μM AU20 RNA monitored at 260 nm. Top and bottom panels, c(S) for MDA5 concentrations below and above 1 μM, respectively. Free AU20 sediments at 2.4 S and free MDA5 at 4.2 S. The limiting peak at 7.4 S (bottom panel) is consistent with a 2:1 MDA5:AU20 complex. (B) Multisignal SV-AUC with 15 μM MDA5 and 1 μM AU20 monitored at 260 nm and with interference optics indicates a 2.6:1 MDA5:AU20 stoichiometry within the complex, based on integration of the areas under the 7.4 S peaks. (C) Global isotherm analysis using the parameters from the curves in (A). The weight-averaged sedimentation coefficient (top), reaction boundary sedimentation coefficient (middle) and population signals of the undisturbed and reaction boundaries (bottom) yielded dissociation constants of 187 and 124 nM for association to AU20 of the first and second MDA5 subunits, respectively. Models enforcing completely independent binding sites (Kd2/Kd1=4) had significantly worse fits (Supplementary Figure S2).