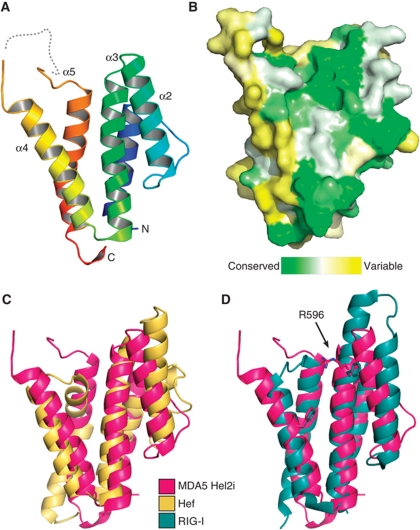
Figure 3.
Crystal structure of the MDA5 helicase-insert (Hel2i) domain. (A) Cartoon representation of MDA5 Hel2i (blue to red, N- to C-terminus). The disordered loop containing the ΔL2 loop deletion is shown as a dashed line. (B) Surface representation coloured according to sequence homology across vertebrate MDA5 sequences (green is conserved, yellow is variable). The view is the same as in (A). (C) MDA5 Hel2i (magenta) has the same overall topology as P. furiousus Hef Hel2i (yellow), with an RMSD of Cα atom positions of 3.8 Å. (D) Comparison of MDA5 Hel2i and duck RIG-I Hel2i (blue). Two residues important for binding of Hel2i to the CARDs in RIG-I (F540 and F571) are shown in stick representation with the corresponding residues for MDA5 (R596 and F630). The extended α3 helix in RIG-I also contributes to the CARD interface. See also Supplementary Table SI.