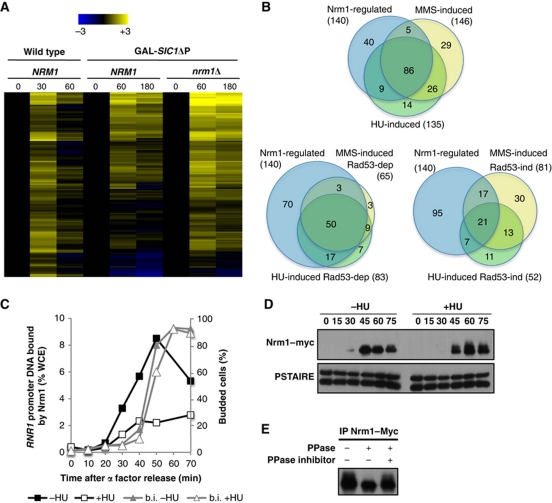
Figure 4.
G1/S genes induced by genotoxic stress are primarily regulated by Nrm1. (A) Heat map showing expression of the 140 Nrm1-regulated G1/S genes. Transcript levels are shown for α-factor-synchronized wild-type cells (30 and 60 min) or wild-type and nrm1Δ cells expressing GAL-SIC1ΔP (60 and 180 min). Transcripts levels are expressed as a log2-fold change relative to the 0-min time point using the colour scale provided (top). (B) Venn diagrams showing the overlap between Nrm1-regulated G1/S genes and either HU- or MMS-induced G1/S genes (top), Rad53-dependent HU- or MMS-induced G1/S genes (left) and Rad53-independent HU- or MMS-induced genes (right). (C) HU abrogates Nrm1 binding to MBF-regulated promoters. Quantitation of Nrm1–myc binding to RNR1 promoter DNA by ChIP in wild-type cells synchronized by α-factor and released into medium with or without 0.2 M HU. Values are shown as a percentage of whole cell extract (WCE). (D) Nrm1 protein is phosphorylated in response to DNA replication stress. Immunoblot of Nrm1–myc from cells from the same time course as in (C). Anti-PSTAIRE is shown as a loading control. (E) Nrm1–Myc immunoprecipitated from cells treated with 0.2 M HU for 1 h was treated with λ phosphatase (PPase) in the presence or absence of phosphatase inhibitors (PPase inhibitor).