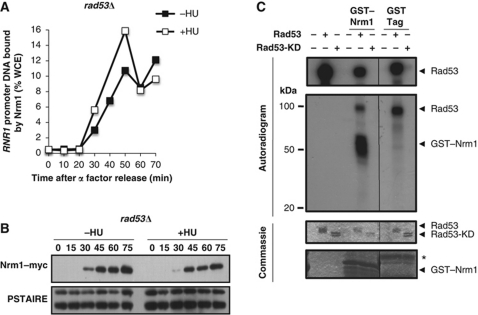
Figure 5.
Rad53, but not Dun1, is required for the Nrm1 inactivation in response to DNA replication stress. (A) Rad53 is required for inactivation of Nrm1 binding to MBF-regulated promoters in response to DNA replication stress. Nrm1–myc binding to RNR1 promoter DNA was determined by ChIP in samples from the same time course as in Figure 1C. Values are shown as percentage of WCE. (B) Rad53 is required for Nrm1 phosphorylation in response to DNA replication stress. Nrm1–myc was detected by immunoblot using cells from the same time course as in Figure 1C. Anti-PSTAIRE is shown as a loading control. (C) Rad53 directly phosphorylates Nrm1 in vitro. Phosphorylated products from an in vitro kinase assay performed using γ-32P-ATP and bacterially expressed recombinant Rad53 protein kinase or mutationally inactivated recombinant Rad53 kinase (Rad53-KD) and either recombinant GST–Nrm1 or GST-tag alone (second panel). Rad53 protein kinase activity is indicated by its autophosphorylation (top panel). Protein levels on the same gel are shown by Commassie Blue staining (lower two panels).