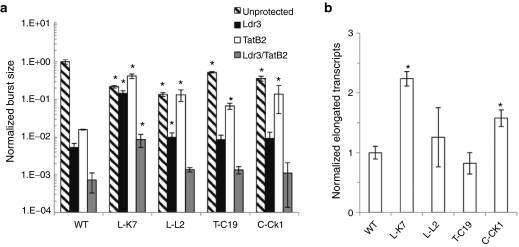
Figure 5.
Mutants develop cross-resistance to RNA interference (RNAi) and increased transcriptional activity. (a) Cells were infected with wild-type (WT) or mutant virus at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.005, and titers were measured every 2 days for 10 days. Viral burst size or cumulative viral replication was calculated by integrating 10-day replication curves (Supplementary Figure S3) and normalized to WT virus in unprotected (UP) cells. Experiments were conducted in biological triplicate, and error bars represent 1 SD. *A significantly different burst size compared to WT virus with the same inhibitory pressure (P < 0.05). (b) Cells were infected with WT or mutant virus at a MOI of 0.025 in the presence of 1 µmol/l saquinivir. Elongated viral transcripts were quantified in technical triplicate via reverse transcriptase quantitative PCR (RT-QPCR) and normalized to β-actin, and the resulting values were normalized to WT virus. Experiments were conducted in biological triplicate, and error bars represent 1 SD. *A significantly higher number of fully elongated transcripts compared to WT virus with the same inhibitory pressure (P < 0.05).