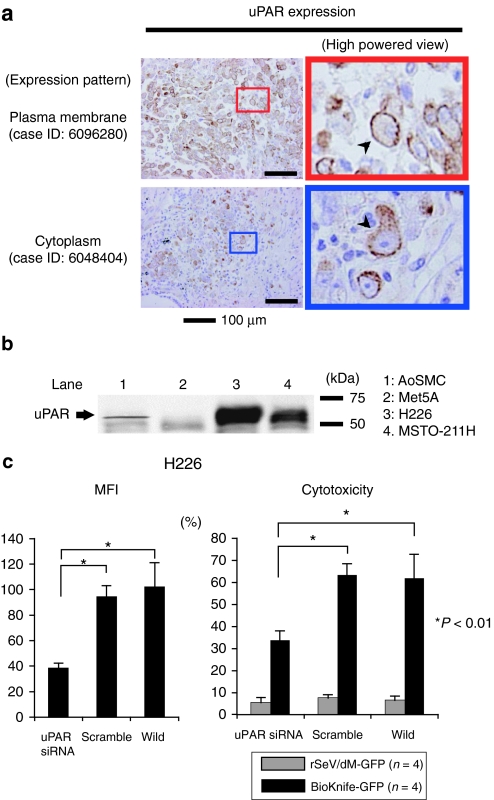
Figure 4.
uPAR expression in MPM cell lines and surgical specimens. (a) Immunohistochemical detection of uPAR expression in MPM surgical specimens (nine cases, summarized in the Supplementary Table S1). Strong immunoreactivity for uPAR expression was found in all cases tested. Note that staining signals were detected on the plasma membrane (upper two photomicrographs, arrowhead) or cytoplasm (bottom two photomicrographs, arrowhead) or both. There was no staining in use of isotype-matched control antibody (data not shown). (b) Representative western blot analysis demonstrated the strong expression of uPAR protein, ~55 kDa, in both MPM cell lines, H226 and MSTO-211H, and a small amount in AoSMCs, but not in normal mesothelial cell Met5A at all. (c) Graphs indicating the essential role of uPAR on the effect of BioKnife-mediated cytotoxicity via siRNA-mediated knockdown. Left graph shows the siRNA-specific downregulation of uPAR expression on cell surface expressed by mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) assessed by flow cytometry. Right graph indicates the corresponding cytotoxic effect of BioKnife-GFP as well as of control virus. Error bars in panels represent the means ± S.D. n = 4/group. AoSMC, human aortic smooth muscle cells; GFP, green fluorescent protein; Met5A, human normal mesothelial cells; MPM, malignant pleural mesothelioma; siRNA, small interfering RNA; uPAR, urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor.