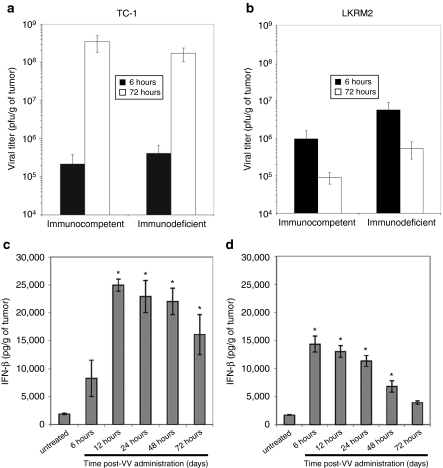
Figure 3.
The ability of our vaccinia virus (VV) vectors to (a, b) replicate and induce (c, d) interferon-β (IFNβ) in flank tumors. (a, c) TC-1 and (b, d) LKRM2 tumor cells were inoculated into the right flanks of syngeneic immunocompetent C57Bl6 or hybrid mice, respectively. The NOD/SCID/γ2 knockout immunodeficient mice were used to study the role of immunological effect. When the tumors reached 300 mm3, 100 million plaque-forming units (pfu) of vaccinia viral vector-expressing mIFNβ (VV.mIFNβ) were injected intratumorally. At various timepoints, tumor tissues were then harvested and assayed for viral replication with plaque assay (a, b) or IFNβ production with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (c, d). The values are expressed as the mean + SEM. *Denotes for significant induction of IFNβ above the untreated control (P < 0.05), which was analyzed with one-way ANOVA.