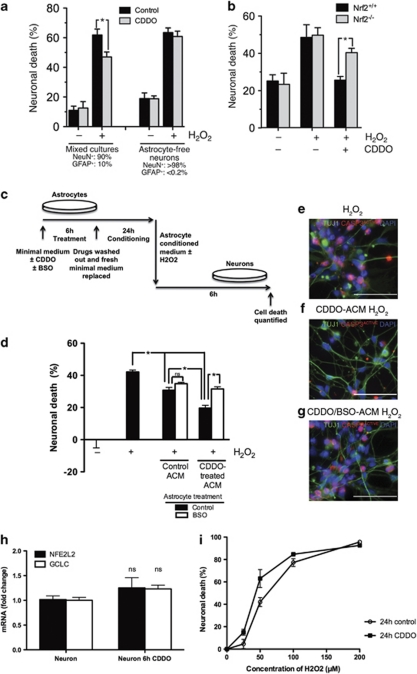
Figure 4.
CDDOTFEA drug treatment is neuroprotective by a GSH-dependent, astrocyte-mediated mechanism. (a) CDDOTFEA-induced neuroprotection requires the presence of astrocytes. Mixed mouse cortical cultures (90% NeuN+ neurons, 10% GFAP+ astrocytes) or astrocyte-free mouse neuronal cultures (>98% NeuN+, <0.2% GFAP+) were treated with CDDOTFEA (100 nM) for 24 h, before treatment with H2O2 (100 μM) for a further 24 h, after which cultures were fixed and levels of cell death assessed. *P<0.05 paired t-test (n=4). (b) CDDOTFEA-induced neuroprotection is Nrf2-dependent. CDDOTFEA-induced neuroprotection in mixed Nrf2+/+ or Nrf2−/− mouse cortical cultures was studied using the same protocols as (a). *P<0.05 paired t-test (n=4). (c) Enriched human astrocyte cultures were treated with CDDOTFEA (250 nM)±BSO (200 μM) for 6 h, the drug washed out, and fresh minimal medium replaced for conditioning over 24 h. ACM was derived as previously and supplemented with H2O2. (d) Human neuronal viability was assessed upon treatment with H2O2 (50 μM) for 6 h, in ACM derived from untreated and CDDOTFEA-treated enriched astrocytes. BSO co-treatment was used to block GCL activity, demonstrating GCL-dependent and -independent neuroprotective effects of ACM. (e–g) Representative TuJ1 and activated caspase-3 co-staining (scale bar, 50 μm). *P<0.05 ANOVA, Newman–Keuls post-test (n=3). (h) Human neuronal expression of NFE2L2 and GCLC mRNA with 6 h CDDOTFEA (250 nM) treatment were examined by quantitative real-time PCR. (i) The effect of treatment with CDDOTFEA (250 nM) for 24 h on human neuronal viability was determined over a range of H2O2 concentrations (0–200 μM, 6 h). *P<0.05 paired t-test (n=3)