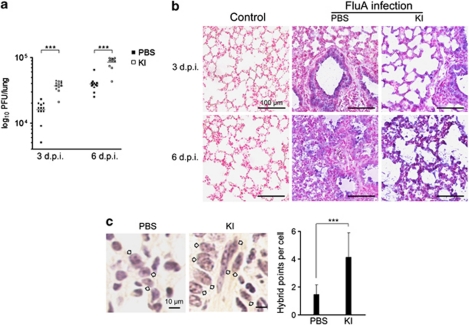
Figure 1.
GzmK blockage aggravates influenza virus infection. (a) The GzmK inhibitor elevates viral load in infected mouse lungs. Balb/c mice were intravenously injected with KI or PBS 1 day before virus infection. Mice were then infected intranasally with Flu A/WSN/33 (H1N1). Viral titers in the infected lungs were quantified using plaque assay at 3 days post-injection (d.p.i.) and 6 d.p.i. KI: GzmK inhibitor. ***P<0.0001. (b) GzmK inhibition aggravates viral infection. The viral protein M2 was detected in the infected lungs by immunohistochemistry (IHC) at 3 and 6 d.p.i. The M2 protein of Flu A/WSN/33(H1N1) was stained blue with NBT/BCIP, and the nucleus was stained red with nuclear fast red. Control mouse lungs were visualized as a negative control. (c) GzmK inhibition rescues viral RNA replication in the infected mouse lungs. Viral M2 RNA was detected by ISH (in situ hybridization) IHC assay. Hybrid points were stained through the DAB system, and the nucleus was stained by hematoxylin. The arrows indicate cells with hybrid points in nuclei. ***P<0.0001. The color reproduction of this figure is available at the Cell Death and Differentiation journal online