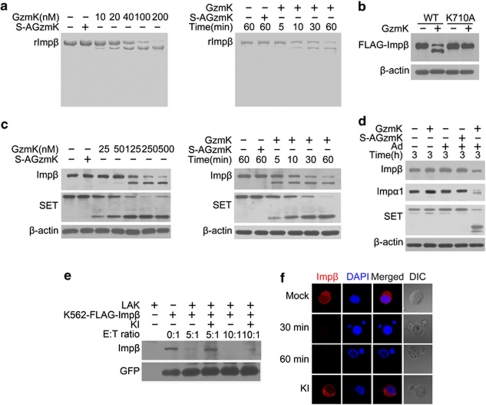
Figure 5.
GzmK also degrades the transport partner importin β after Lys710 (a) GzmK directly cleaves recombinant importin β (rImp β) in a dose- and time-dependent manner. rImpβ (0.5 μM) was incubated with different concentrations of GzmK for 1 h or with 10 nM GzmK for the indicated times at 37°C followed by Coomassie staining. (b) GzmK cleaves importin β at Lys710. Wild-type (WT) and FLAG-K710A-Imp β were transiently expressed in 293 T cells for 48 h. Cell lysates (2 × 105 equivalents) were treated with 0.5 μM GzmK for 15 min and detected by anti-FLAG mAb. β-Actin was used as a negative control. (c) GzmK proteolyzes the native importin β of cell lysates in a dose- and time-dependent manner. K562 cell lysates (2 × 105 equivalents) were incubated with different concentrations of GzmK for 1 h or with 0.5 μM GzmK for the indicated times at 37°C. SET was probed as a positive control and β-actin was used as a negative control. (d) GzmK cleaves importin β in GzmK-loaded intact cells. Jurkat cells were incubated with 1 μM GzmK and Ad (100 PFU/ml) for 3 h at 37°C and probed for importin β, importin α1, SET, and β-actin. (e and f) GzmK cuts importin β during the LAK cell-mediated killing process. K562 cells expressing FLAG-Impβ were incubated with IL-2-activated LAK cells at the indicated E/T ratios followed by immunoblotting. GFP was specifically expressed in K562 cells and visualized as a loading control (panel e). Importin β was probed with anti-FLAG mAb (red) using immunofluorescence assay (panel f). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). DIC: differential interference contrast. The color reproduction of this figure is available at the Cell Death and Differentiation journal online