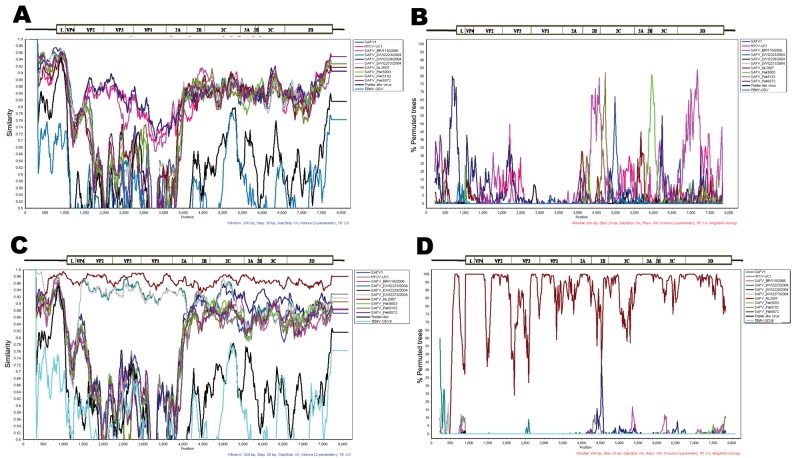
Figure A1.
Recombination analyses of Saffold cardioviuses (SAFVs), isolated in Beijing, China, 2007–2009. The relationships among the aligned cardiovirus genome sequences were analyzed by SimPlot software version 3.5.1 (11). A) Sliding-window SimPlot graph generated by using the sequence of the BCHU79 (SAFV-2) as a query against SAFVs, Theiler-like virus, and Theiler murine encephalomyelitis virus–GDVII. B) Bootscan analysis of the sequence of SAFV BCHU79 in comparison to SAFVs, Theiler-like virus, and Theiler murine encephalomyelitis virus–GDVII. C) Sliding-window SimPlot graph generated by using the sequence of the BCH1031 (SAFV-3) as a query against SAFVs, Theiler-like virus, and Theiler murine encephalomyelitis virus–GDVII. D) Bootscan analysis of the sequence of SAFV BCH1031 in comparison to SAFVs, Theiler-like virus, and Theiler murine encephalomyelitis virus–GDVII. Because the genome sequence identity between BCH1031 and BCH115 is as high as 94%, BCH1031 was used to conduct the SimPlot analysis. The nucleotide position is given on the x-axis, and the percent nucleotide sequence similarity is given on the y-axis. The positions relative to viral genes are shown by genome diagrams above the plots and scans. SAFV-1 (prototype), SAFV-2 UC1, SAFV-2 D/VI/2229/2004, SAFV-2 BR118/2006, SAFV-3 D/VI/2273/2004, SAFV-3 D/VI/2223/2004, SAFV-3 NL2007, SAFV-5 Pak5003, SAFV-5 Pak5152, SAFV-6 Pak 6572, Theiler-like virus NGS910, and Theiler murine encephalomyelitis virus–GDVII were used as reference sequences (GenBank accession nos. NC009448, NC010810, EU681176–EU681179, FM207487, FJ463615–FJ463617, AB090161, and X56019).