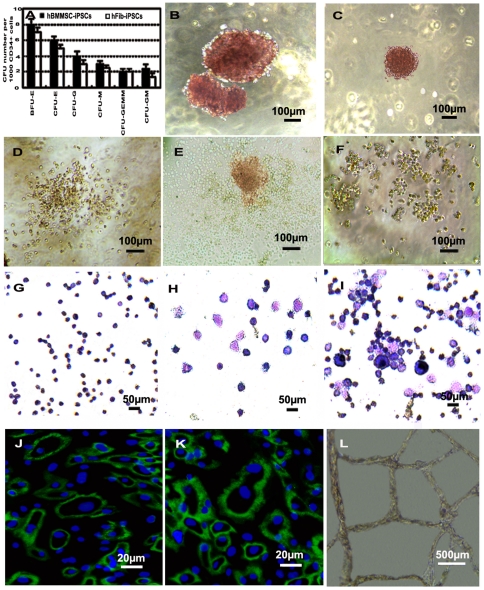
Figure 5. Hematopoietic and endothelial cell potential assay of CD34+ progenitor cells obtained from differentiated hBMMSC-iPSCs.
(A-I) Hematopoietic CFU formation and hematopoietic lineages assay for the potential of CD34+ progenitor cells. (A) Measurement for CFU potential of CD34+ cells derived from hBMMSC-iPSCs compared to that from hFib-iPSCs. (B-F) Various types of CFUs were observed with a reversed telescope as BFU-E (B), CFU-E (C), CFU-GM (D), CFU-GEMM (E) and CFU-G (F) when CD34+ progenitor cells derived from hBMMSC-iPSCs were seeded into CFU forming culture system to assess the short-term differentiation capabilities of hematopoietic progenitors. (G-I) Morphologies of the hematopoietic lineages derived from CFU culture of CD34+ progenitor cell commitment to hematopoietic cells observed with a reversed telescope (Olympus), including erythroid from BFU-E (G), granulocyte from CFU-G (H) and macrophage, granulocyte, erythroid, megakaryocyte from CFU-GEMM (I). (J-L) Analysis of endothelial cell potential of CD34+ progenitor cells derived from hBMMSC-iPSCs. Some of CD34+ progenitor cells cultured with EGM-2 were positive to CD31 (J) and VE-CADHERIN (K). When treated with VEGF-A on Matrigel for 3 days, vascular-like structures were photographed (L).