Figure 4.
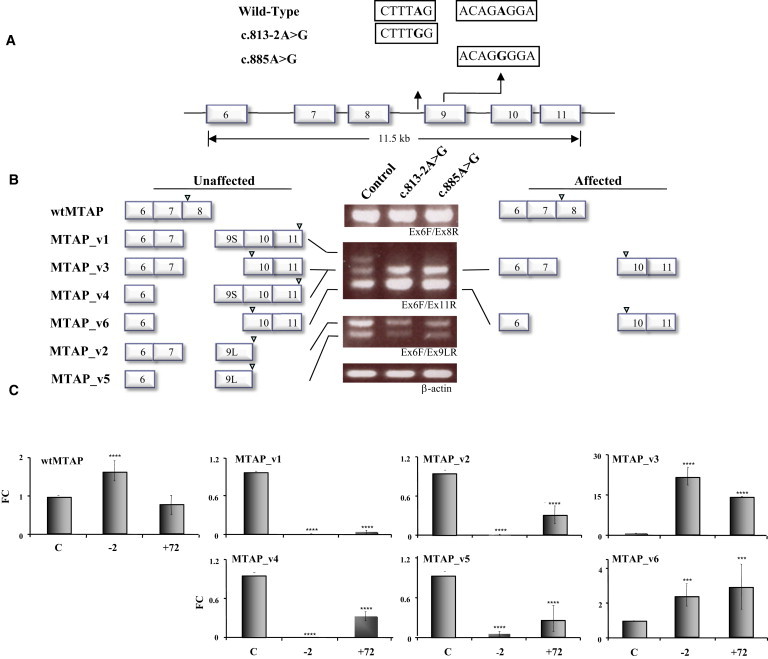
Patient-Derived MTAP Mutations Result in Exon Skipping
(A) Sequence differences of the three minigene constructs, WT, c.813-2A>G, and c.885A>G, are highlighted.
(B) Schematic representation of the major sequence-verified isoforms flanking the electrophoretic profile of each minigene construct. Arrowheads above exons depict the positions of translational stop codons. The WT construct expresses all alternative splice variants that are detectable with this combination of primers (exon 6 forward [Ex6F] and exon 11 reverse [Ex11R]) (left), whereas patient-derived mutant constructs, c.813-2A>G and c.885A>G, expressed relatively very low levels of exon-9S- and -9L-containing variants, v1/v4 and v2/v5, respectively. By comparison, the expression of isoforms v3 and v6 was markedly elevated in both mutant constructs.
(C) qRT-PCR analysis of archetype MTAP and isoform expression in cells that express each of the minigene constructs. Expression analysis of the three minigene constructs demonstrated that the c.813-2A>G mutant construct resulted in significantly increased archetype MTAP expression levels, whereas both the c.813-2A>G and c.885A>G mutant constructs were associated with an absence of and/or significantly decreased levels of MTAP_v1, _v2, _v4, and _v5. Both mutant constructs resulted in significantly increased expression levels of MTAP_v3 and _v6. The following abbreviation is used: wtMTAP, archetype MTAP. The error bars represent the averages of three independent experiments.
