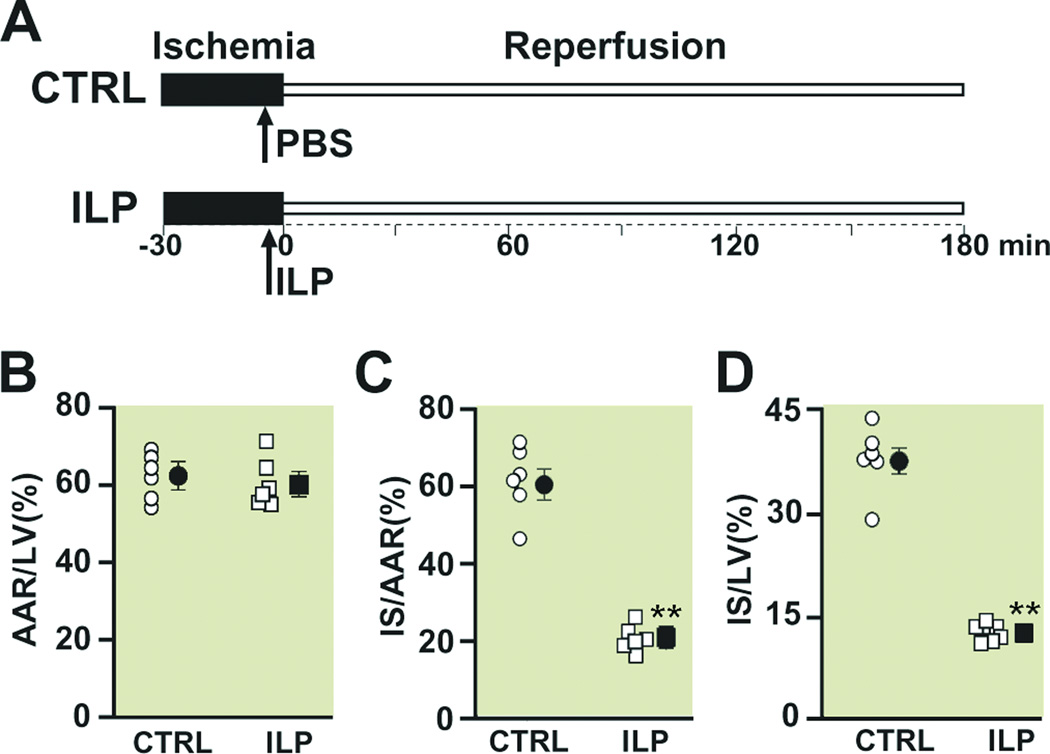
Figure 1. Intralipid administration reduces the infarct size in the in vivo ischemia/reperfusion rat model.
A. experimental protocol, the left coronary artery was occluded for 30 minutes followed by 3 hr of reperfusion. One single IV bolus of Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) (control group, CTRL) or 20% Intralipid (5ml/kg body weight, ILP) was administered 5 min before reperfusion. Percentage of area at risk (AAR) divided by left ventricle (LV) (B), infarct size (IS) divided by AAR (C), and infarct size (IS) divided by left ventricle in CTRL (circles) and Intralipid (squares). The individual measurements (n=6 in ILP and n=6 in CTRL) are shown in open shapes whereas the averages (Mean±SEM) are shown in filled shapes **P<0.01 vs. CTRL.