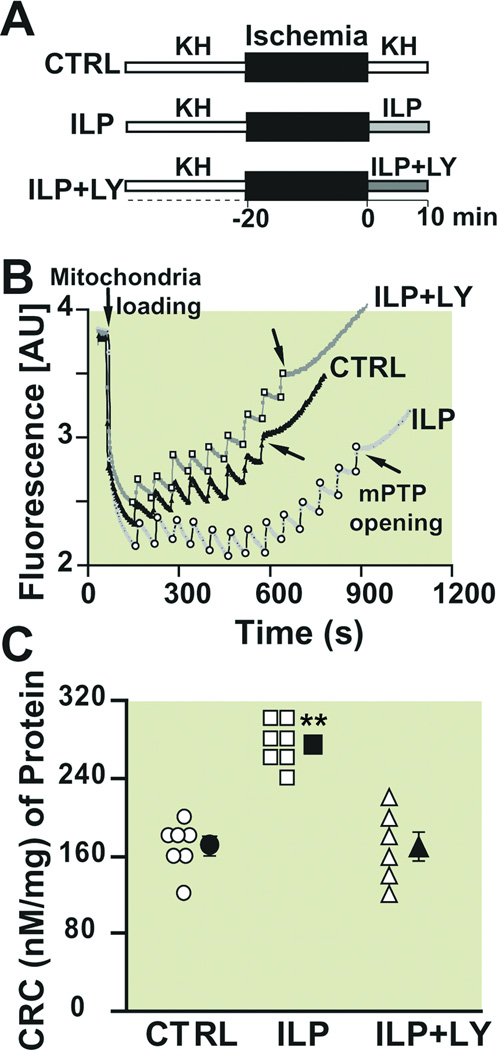
Figure 6. Intralipid inhibits the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore and this inhibition is abolished by PI3K inhibitor.
A. Experimental protocol for measuring calcium retention capacity. At the onset of reperfusion, isolated hearts are perfused with Krebs Henseleit (KH, control group, CTRL), 1% Intarlipid (ILP) or 1% Intralipid+LY294002 (ILP+LY) for 10 min. B. Typical recording of the mitochondria permeability transition pore opening in isolated mitochondria from control (black trace), ILP (light gray trace) and ILP+LY (dark gray trace). Fourteen pulses (gray arrows) of 20 nM calcium were required to trigger the opening of mitochondria permeability transition pore in ILP group compared to 7 pulses (black arrows) in CTRL and 8 pulses in ILP+LY. C. Calcium retention capacity (CRC) in CTRL (circles, n=7), ILP (squares, n=7) and ILP+LY (triangles, n=6). The individual measurements in each groups are shown in open shapes whereas the averages (Mean±SEM) are shown in filled shapes.**P<0.01 vs. CTRL and ILP+LY.