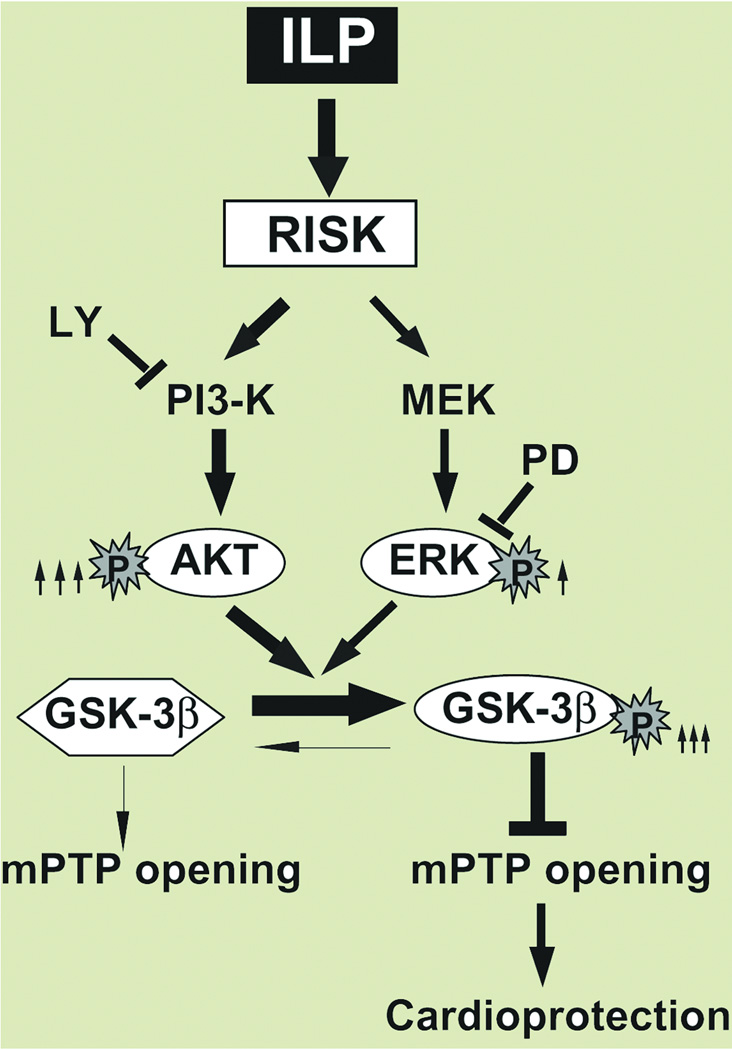
Figure 7. Proposed mechanisms underlying Intralipid-induced cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion injury.
The Reperfusion Injury Salvage Kinases (RISK) pathway is activated in the presence of Intralipid (ILP), resulting in increased phosphorylation of both Akt and ERK, although the degree of activation is much more prounnced in Akt (8 fold, shown by thick arrow) than in ERK (3 fold, shown by thin arrow). Both pathways converge to phosphorylate GSK-3β (inactive form), which in turn inhibits the opening of the mPTP and induces protection against reperfusion injury. The protection provided by Intralipid is fully abolished by the PI3K specific inhibitor, LY294002 (LY) and partially by PD98059 (PD).