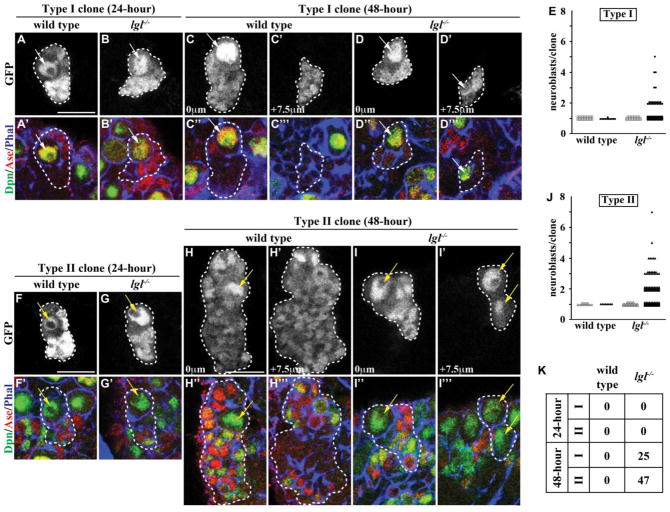
Figure 1. lgl is required for the maintenance, but not specification, of progenitor cells.
(A–B) At 24 hours after clone induction, type I neuroblast clones in both wild-type and lgl334/3644 mutant brains contained a single neuroblast surrounded by GMCs and neurons. (n = 30 and 28 clones, respectively) (C–D) At 48 hours after clone induction, type I neuroblast clones in wild-type brains still contained a single neuroblast surrounded by GMCs and neurons; however, type I neuroblast clones in lgl334/3644 mutant brains contained a parental neuroblast immediately adjacent to GMCs and neurons with supernumerary neuroblasts located in the basal portion of the clone. (n = 11 and 91 clones, respectively) (E) Quantification of the number of neuroblasts per type I neuroblast clone is shown for wild-type and lgl mutant clones at 24 (open) and 48 (filled) hours after clone induction. (F–G) At 24 hours after clone induction, type II neuroblast clones in both wild-type and lgl334/3644 mutant brains contained a single neuroblast surrounded by immature INPs, INPs, GMCs and neurons. (n = 15 and 25 clones, respectively) (H–I) At 48 hours after clone induction, type II neuroblast clones in wild-type brains still contained a single neuroblast surrounded by immature INPs, INPs, GMCs and neurons; however, type II neuroblast clones in lgl334/3644 mutant brains contained a parental neuroblast isolated from the supernumerary neuroblasts by many immature INPs, INPs, GMCs and neurons. (n = 8 and 144 clones, respectively) (J) Quantification of the number of neuroblasts per type II neuroblast clone is shown for wild-type and lgl mutant clones at 24 (open) and 48 (filled) hours after clone induction. (K) The table shows the frequency of clones containing supernumerary neuroblasts. Brains were stained with the indicated markers. Single neuroblast clones marked by GFP are circled by the dotted line. Arrows indicate the neuroblasts (white, Type I; yellow, Type II). Single confocal planes of the same clone are shown at 0 mm and +7.5 mm (C–D and H–I). All scale bars are 10 μm.