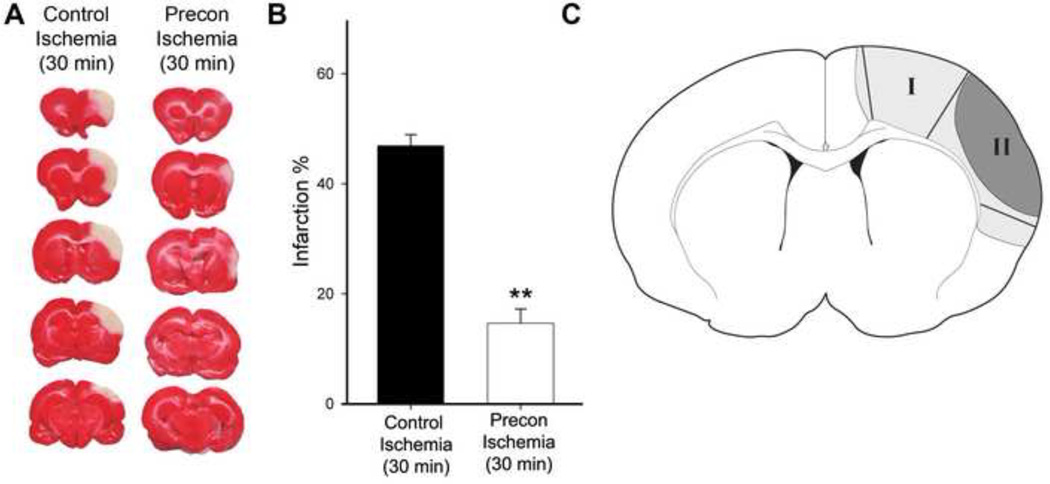
Fig. 1. Rapid preconditioning inhibited infarct size.
A. Representative infarction with TTC staining. Ischemic brains were harvested 2 d after stroke for TTC staining, sectioned into 5 blocks, and stained with TTC solution. B. Bar graphs (the right column) representing the average infarction size normalized to the non-ischemic cortex. N=7/group. ** vs control ischemia (30 min), P<0.01. C. Diagram showing the ischemic tissues corresponding to ischemic penumbra and core that were dissected for analysis. Ischemic penumbra (region I) is defined as the ischemic region spared by preconditioning; the ischemic core (region II) refers to the ischemic area that develops into infarction in animals receiving preconditioning and test ischemia. In the test ischemic group, a line defining the ischemic border was drawn 1.5 mm lateral to the midline. From this line, an approximately 2mm wide area of ischemic tissue was dissected as region I. The remaining ischemic tissue after dissection of region I was dissected as the ischemic core. The corresponding regions in the preconditioning animals were dissected as ischemic penumbra and core.