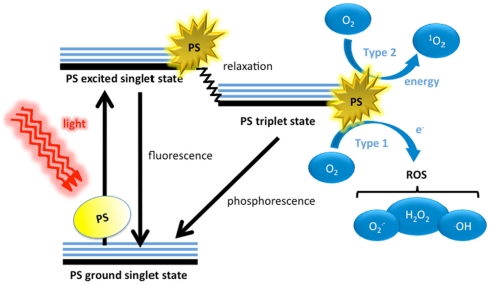
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of photodynamic therapy including the Jablonski diagram. The PS initially absorbs a photon that excites it to the first excited singlet state and this can relax to the more long lived triplet state. This triplet PS can interact with molecular oxygen in two pathways, type I and type II, leading to the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and singlet oxygen respectively.