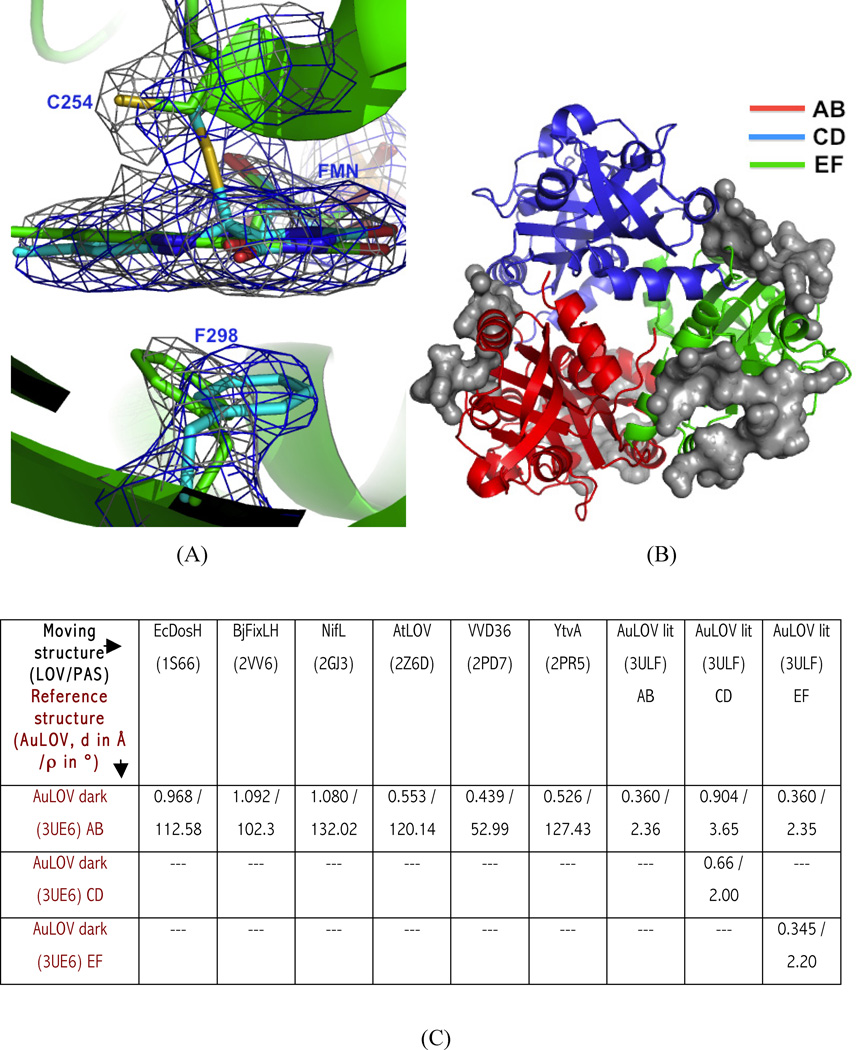
Figure 2.
Dark and light state structures of AuLOV. (A) Overlay of 2Fo-Fc map in the dark (grey) and light structures (blue); both maps contoured at 1.4 σ. The most substantial light-induced change in the vicinity of FMN is found at Phe298, located underneath the FMN plane; it moves in the opposite direction upon light-irradiation; (B) Residues in the asymmetric unit involved in intermolecular contacts are highlighted (as grey surface). Crystal contacts with the other ASUs are observed only in the AB (red) and EF (green) dimers. The CD dimer (blue) is least constrained by the crystal lattice and makes contact only with the AB and EF dimers; (C) The monomer orientation of AuLOV in dark state is compared with other LOV/PAS-containing dimers, using rigid body screw-axis-rotation analysis. Screw rotation parameters [rotation (ρ) in degrees and translation (d) in angstroms] are given for each pairwise comparison with respect to AuLOV. See also Figures S2 and S3.