Figure 6.
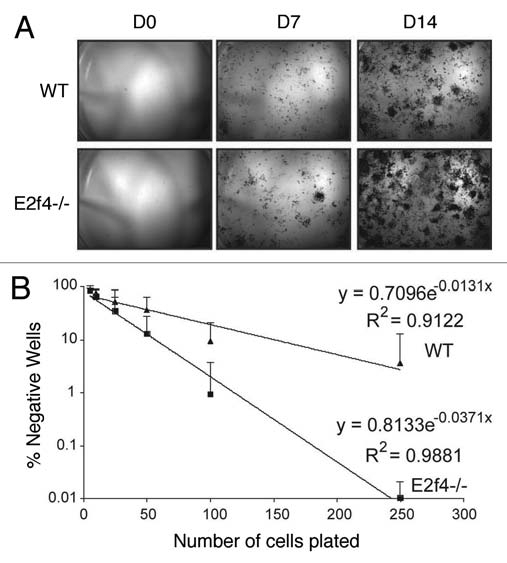
E2f4-/- calvarial preparations contain more ALp-progenitor osteoblasts than wildtype preparations. (A) Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining of calvarial cells. Cells isolated from calvaria were sparsely plated in induction media and stained for ALP activity at the indicated time points. E2f4-/- embryo derived calvarial cells produce more alkaline phosphatase-positive colonies, likely derived from osteoblast progenitors, than wildtype embryo derived cells (n ≥ 5). (B) Limiting dilution assay of wildtype and E2f4-/- calvarial cells. Cells were plated directly into induction media and alkaline-phosphatase-positive colony number was assessed 7 days later. The graph shows an average of 9 independent experiments, error bars indicate one standard deviation. E2f4-/- calvarial cultures exhibited a higher clonal frequency of alkaline phosphatase-positive colonies in comparison with wildtype derived cultures.
