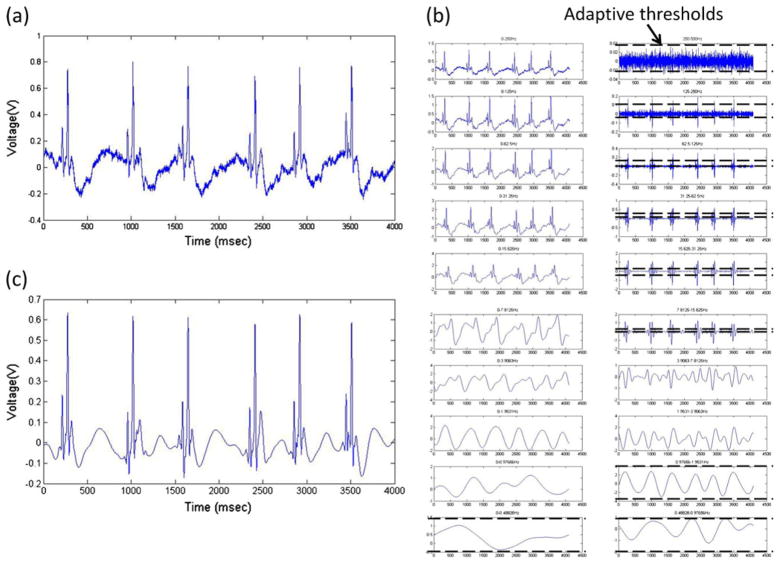
Fig. 3.
Wavelet transform and noise-reduction algorithm for zebrafish ECG recordings. (a) Raw signal directly recorded from sedated zebrafish at sampling rate of 1000 Hz. (b) Breakdown of raw signals into frequency segments via coif5 wavelet transform. Low frequency signals (DC to 0.98 Hz) were completely filtered. Thresholds were applied to the individual frequency ranges for suppression of corresponding noise levels. Sub-threshold values were set to zero. Signals within frequency range from 0.98 Hz to 7.81 Hz were reserved to ensure fidelity of T-waves. (c) Filtered ECG signals were reconstructed by performing inverse wavelet transform from processed frequency segments