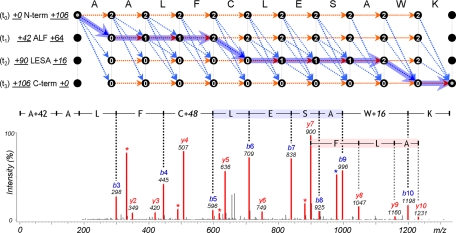
Fig. 6.
Dynamic programming to identify triply modified peptide, A+42ALFC+48LESAW+16K, and its MS/MS spectrum. First, two sequence tags, ALF (t1) and LESA (t2), were derived from the spectrum. The t0 and t3 tags are special tags of length zero that define the start and end nodes of dynamic programming. Numeric figures at both ends of a tag represent mass differences (Δ mass) between the tag's flanking mass and the mass of subsequence corresponding to the flanking mass region: the left figure for N terminus and the right figure for C terminus. They represent the total modified mass of the region. To restrict jumps between nodes, nodes are labeled according to the position of matched tag: 0 for before the tag, 1 for inside the tag, and 2 for after the tag. Dashed arrows represent all possible jumps satisfying constraints on the sequence tags and the highlighted path represents the optimal alignment. For a modification jump, its modified mass is defined as a difference between N-terminal Δ mass values of two tags.