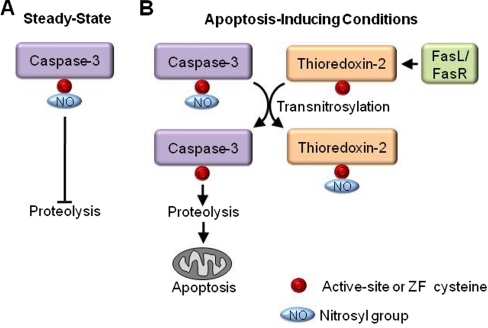
Fig. 1.
Crosstalk between catalytic activity and redox regulation. Caspase-3 is the terminal protease in the apoptosis cascade and cleaves numerous proteins to complete apoptosis. A, Under steady-state conditions the catalytic cysteine of caspase-3 is nitrosylated which inhibits its protease activity and prevents apoptosis (1). B, When tumor necrosis factor family member FasL binds to its cognate receptor FasR to trigger apoptosis, thioredoxin-2 transnitrosylates mitochondrial-associated caspase-3 derepressing its catalytic activity and promoting apoptosis (2).