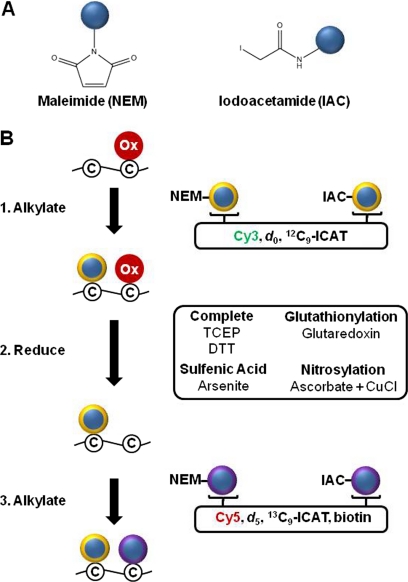
Fig. 6.
Differential alkylation indirectly detects oxidation and is modular. A, Structures of the maleimide and iodoacetamide functional groups. Bifunctional thiol specific reagents combine these two groups with fluorescent, stable isotope, or epitope tags (blue circles). B, The differential alkylation procedure labels nonoxidized cysteine thiols before (yellow ring) and after (purple ring) reduction with two different alkylation reagents to determine the percent of the cysteine that is reversibly alkylated. Fluorescent reagents include Cy3 and Cy5 tags and stable isotope labeled regents include d0 and d5 NEM or 12C9-ICAT and 13C9-ICAT reagents. Alkylation with an untagged alkylation reagent followed by a biotinylated thiol-specific reagent allows enrichment of reversibly oxidized peptides or proteins. Complete reduction of all reversibly oxidized cysteines can be achieved with TCEP or DTT. Selective reduction of specific cysteine oxoforms is possible using ascorbate plus CuCl to reduce S-nitrosylation, the enzyme glutaredoxin to reduce glutathionylation, and arsenite to reduce sulfenic acid.