Figure 2.
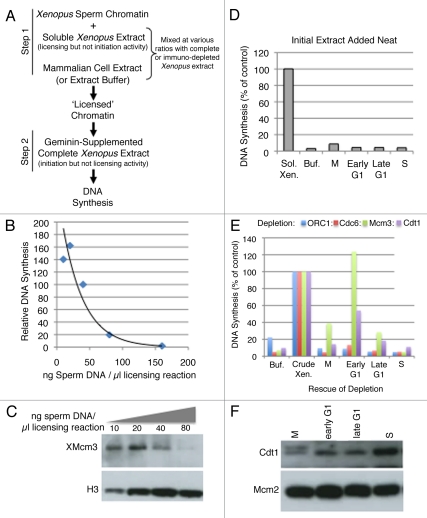
A heterologous system for the identification of licensing activities. (A) Description of licensing assay protocol (see text and methods for details). (B) Various concentrations of sperm chromatin were added to soluble high-speed Xenopus extract in Step 1, followed by the addition of sufficient geminin-supplemented complete (low-speed) extract to maintain a constant sperm template concentration in Step 2 of 13.3 ng/µl. The relative fraction of input DNA synthesized was plotted as a function of original template concentration in Step 1. This experiment identifies the Step 1 template concentration at which licensing components (e.g., Mcm2–7) become limiting for DNA synthesis. 40 ng/µl was used in all subsequent experiments. (C) Immediately following Step 1 from (B), sperm chromatin was isolated from aliquots of the reaction by centrifugation through a sucrose cushion. Chromatin bound proteins from equivalent amounts of sperm DNA from each reaction were subjected to immuno-blotting to detect the amount of chromatin-loaded Mcm proteins. (D) In Step 1, soluble high-speed Xenopus egg extract was replaced with either Buffer (Buf) or soluble extracts from CHO cells at different times during the cell cycle (M = mitosis or cells at shake-off; Early G1 = 2 hours after mitosis; Late G1 = 7 hours after mitosis; S = S phase; cells released from mitosis into aphidicolin for 16 hours and released from the aphidicolin block for one hour). CHO extracts cannot license Xenopus sperm chromatin on their own, regardless of the time during the cell cycle at which they are prepared. (E) Soluble high-speed Xenopus egg extracts were depleted of ORC1, Cdc6, Mcm3 or Cdt1 and Step 1 of the licensing reaction was performed with mixtures of depleted extract and either Buffer (Buf) or CHO cell extracts (Xenopus: Mammalian extract ratio 1:3) prepared at the indicated times during the cell cycle as in (D). As positive control reactions, depleted Xenopus extracts were supplemented with partially purified fractions of Xenopus egg extract (Crude Xen.: PEG-M for Mcm3 depleted extracts and PEG-B for all others; reference 18) and all reactions were quantified relative to this positive control. (F) Soluble hamster extracts used in (E) were subjected to immuno-blotting to examine the level of hamster Cdt1 and Mcm proteins.