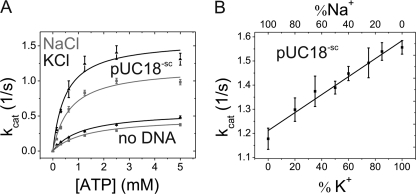
FIGURE 2.
Effect of K+ and Na+ ions on steady-state ATPase activity of gyrase. A, dependence of the steady-state ATPase rate on the ATP concentration. The Km values in the presence of Na+ (gray) or K+ (black) are virtually identical without DNA (1.3 ± 0.2 mm with Na+ and 1.3 ± 0.2 mm with K+) and in the presence of supercoiled plasmid DNA (0.66 ± 0.13 mm with Na+ and 0.5 ± 0.2 mm with K+). There was no significant stimulation of the ATPase activity by potassium ions without DNA (kcat = 0.46 ± 0.02 s−1 for Na+ and 0.59 ± 0.03 s−1 for K+) or in the presence of 100 nm pUC18 (kcat = 1.19 ± 0.07 s−1 for Na+ and 1.58 ± 0.13 s−1 for K+). Error bars denote S.D. from three independent experiments. B, steady-state ATPase activity as a function of K+/Na+ buffer composition in the presence of 80 nm pUC18 plasmid DNA. The low ATPase activity at 100 mm NaCl increased linearly with increasing K+ content. Error bars denote S.D. from three independent experiments.