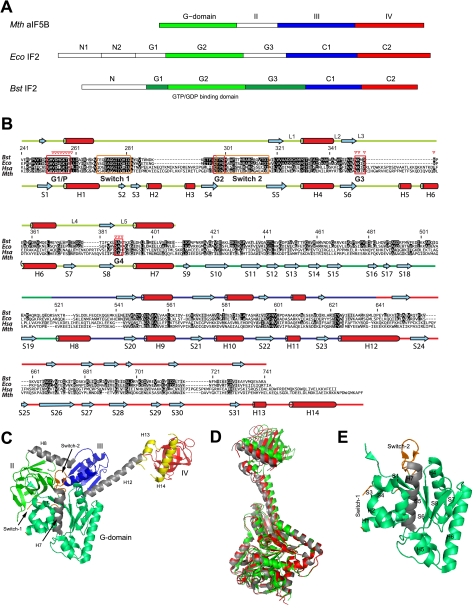
FIGURE 1.
Domain organization of IF2 and aIF5B. A, domain nomenclature for IF2 homologs from M. thermoautotrophicum (Mth), E. coli (Eco), and B. stearothermophilus (Bst). B, sequence alignment for IF2 homologs from B. stearothermophilus (Bst), E. coli (Eco), Homo sapiens (Hsa), and M. thermoautotrophicum (Mth). Amino acid numbering is for B. stearothermophilus IF2. More and less conserved residues are depicted in black and gray, respectively. Below the sequence alignment the helices (H) and β-strands (S) found in M. thermoautotrophicum aIF5B crystal structures are indicated, connected by colored lines, representing IF2-G2 (light green), IF2-G3 (dark green), IF2-C1 (blue), and IF2-C2 (red). Above the sequence alignment the secondary structure elements as found by NMR on B. stearothermophilus IF2 are shown. Guanine nucleotide binding boxes G1–G4, loops L1-L5, and Switch-1 and Switch-2 regions are indicated; red triangles indicate residues that contact the ligand. C, M. thermoautotrophicum aIF5B domain organization. Domain-connecting helices H7, H8, and H12 are colored gray; Switch-1 and Switch-2 are colored orange. Two C-terminal a/eIF5B helices H13 and H14, not occurring in B. stearothermophilus IF2, are colored yellow. D, crystal structures for the free (gray), the GDP-bound (red), and the GDPNP-bound (green) states of M. thermoautotrophicum aIF5B fit on the G2 domain backbone (excluding the Switch-1 and Switch-2 regions). E, secondary structure elements of the M. thermoautotrophicum aIF5B-G2 domain.