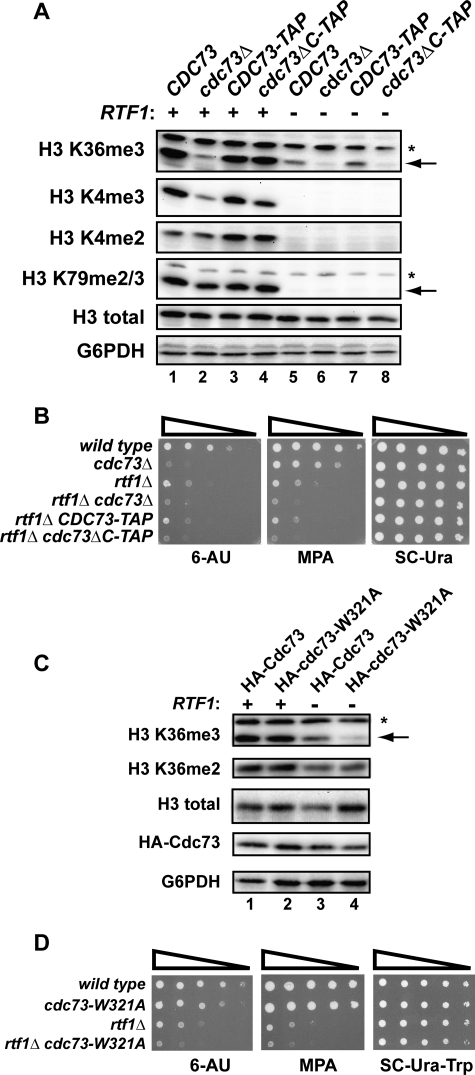
FIGURE 6.
Deletion of both the Cdc73 C-domain and Rtf1 leads to enhanced mutant phenotypes and defects in histone modifications. A and C, Western analysis on extracts from strains with the indicated genotypes (KY1021, KY1857, KY1799, KY1791, KY1802, KY703, KY1797, and KY1789) to detect levels of Paf1C-dependent H3 modifications. The arrows indicate the band of interest, and nonspecific bands are marked by an asterisk. B and D, dilution analyses assessing 6-AU and MPA sensitivity of the indicated strains (KY1021, KY1857, KY1802, KY703, KY1797, and KY1789). 10-Fold dilutions starting from 1.0 × 108 cells/ml were spotted to medium containing 6-AU or MPA and incubated at 30 °C for 2 days (D, SC−Ura−Trp), 4 days (B and D, 6-AU), or 8 days (D, MPA). For C and D, cdc73Δ (KY1858) or cdc73Δ rtf1Δ (KY2195) strains were transformed with TRP1-marked CEN/ARS plasmids that express either HA-tagged Cdc73 or HA-tagged Cdc73-W321A. Transformants were grown on media lacking tryptophan.