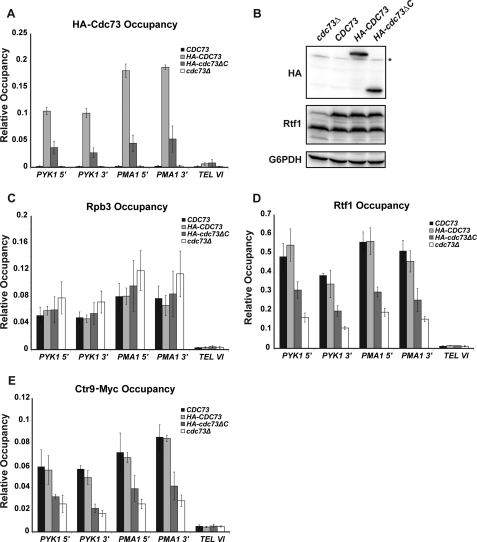
FIGURE 7.
Deletion of the Cdc73 C-domain reduces Paf1C occupancy on actively transcribed genes. ChIP analysis of HA-tagged Cdc73 (A), Rpb3 (C), Rtf1 (D), and Myc-tagged Ctr9 (E) was measured at the 5′ end of PYK1 (+253 to +346, relative to ATG), 3′ end of PYK1 (+1127 to +1270), 5′ end of PMA1 (+214 to +319), 3′ end of PMA1 (+2107 to +2194) and at an untranscribed region proximal to the telomere of chromosome VI (TEL VI; chromosome coordinates 269,495–269,598). Values represent the average of at least three independent samples with S.D. (error bars). B, Western analysis of HA-tagged Cdc73 levels in strains utilized for ChIP. Extracts from a cdc73Δ strain (KY1858) transformed with empty vector or plasmids expressing full-length untagged Cdc73, full-length HA-tagged Cdc73, or truncated HA-tagged Cdc73ΔC were probed with antibodies specific for the HA tag (Cdc73), Rtf1, or glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) as a loading control. *, nonspecific band. The two bands detected with the Rtf1 antiserum represent full-length Rtf1 and a consistently observed breakdown product.