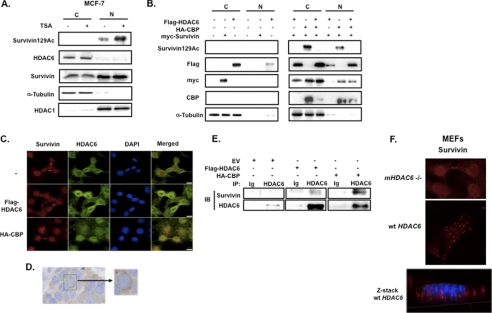
FIGURE 3.
HDAC6 deacetylates survivin for its nuclear export. A, MCF-7 cells were treated with 1 μm TSA or vehicle control for 6 h. Nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) lysates were prepared by subcellular fractionation then immunoblotted with anti-acetylated survivin, anti-survivin, anti-HDAC6, α-tubulin, and HDAC1, the latter two of which were cytoplasmic and nuclear fraction controls, respectively. B, HEK293 cells were co-transfected with FLAG-HDAC6, HA-CBP, and Myc-survivin. Nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) lysates were prepared and immunoblotted (IB) with anti-acetylated survivin, anti-FLAG, anti-Myc, anti-CBP, and anti-tubulin. C, HeLa cells were co-transfected with FLAG-HDAC6, HA-CBP, or empty vector (−) and then fixed and co-immunostained with anti-survivin (red), anti-HDAC6 (green), and DAPI. Cells were imaged by a Nikon confocal microscope. Scale bars, 20 μm. D, 4 μm paraffin-fixed estrogen-receptor positive breast cancer tissue was immunostained with anti-HDAC6, as described previously (23). E, HeLa cells were transfected with FLAG-HDAC6, HA-CBP or empty vector (EV) then immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-HDAC6 or immunoglobulin control (Ig) and immunoblotted with anti-survivin and anti-HDAC6. F, MEFs isolated from mHDAC6 null (−/−) or WT mice were immunostained with anti-survivin (red) and imaged by a Nikon confocal microscope. Scale bar, 20 μm. Optical sectioning through the depth of the cell was performed using z-stacking (red, survivin; blue, DAPI).