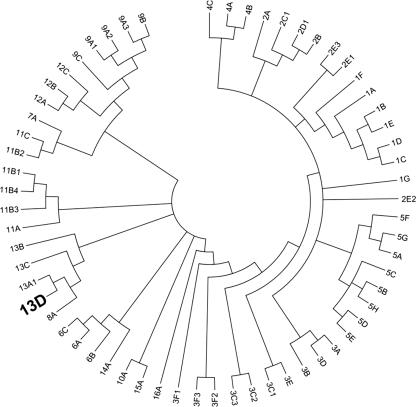
FIGURE 7.
Evolutionary relationship of new AKR13D from R. serpentina to annotated AKR families and subfamilies. The dendrogram shows the topological relationships between AKR subfamilies. The new AKR13D from R. serpentina is most closely related to other members of the AKR13 family and AKR8. The evolutionary history of all annotated AKRs including the new AKR from R. serpentina was inferred using the neighbor joining method (43). A bootstrap consensus tree was inferred from 1000 replicates (44), with subfamily branches collapsed where possible. Branches corresponding to partitions reproduced in less than 30% bootstrap replicates were also collapsed. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Poisson correction method (45) and are in the units of the number of amino acid substitutions per site. All of the positions containing alignment gaps and missing data were eliminated only in pairwise sequence comparisons (pairwise deletion option). There were a total of 607 positions in the final data set. Phylogenetic analyses were conducted in MEGA4 (46).