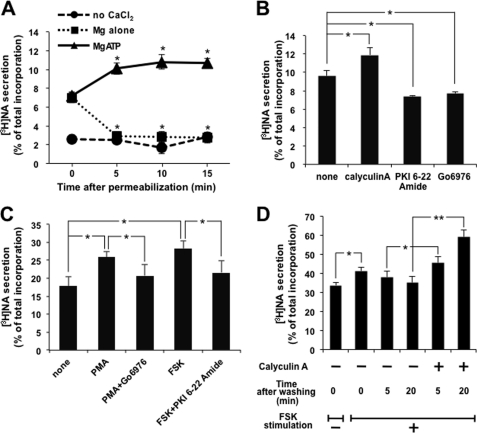
FIGURE 1.
Protein phosphorylation is involved in the regulation of exocytosis. A, PC12 cells labeled with [3H]NA were permeabilized with 10 μm digitonin and then maintained at room temperature for the period indicated in the presence or absence of 2 mm MgATP. [3H]NA secretion was triggered by adding 2 mm CaCl2 to give a free Ca2+ concentration of 1 μm for 2 min. NA release is indicated as the percentage of released [3H]NA relative to the total [3H]NA incorporated into the cells. B, after digitonin permeabilization, [3H]NA-labeled PC12 cells were incubated at room temperature for 5 min in the presence of 2 mm MgATP, along with either calyculin A (100 nm), PKI 6-22 amide (100 nm), or Go6976 (1 μm). [3H]NA secretion by 1 μm Ca2+ for 2 min was assayed. C, PC12 cells labeled with [3H]NA were treated with PMA (1 μm) or forskolin (FSK) (50 μm) with or without each inhibitor for 30 or 5 min, respectively, followed by the assay of [3H]NA secretion by high K+ solution (70 mm KCl) for 2 min. D, PC12 cells labeled with [3H]NA were treated with 50 μm FSK for 5 min. After removal of the stimulus, cells were left for 5 or 20 min in the presence or absence of 100 nm calyculin A, followed by the assay of [3H]NA secretion by 10 μm ionomycin for 5 min. All of the results are the means ± S.E. (error bars) of five independent experiments. Student's t tests were used, and significance is represented by * or ** for p < 0.05 or p < 0.01, respectively. The same statistical methods were applied to the following results.