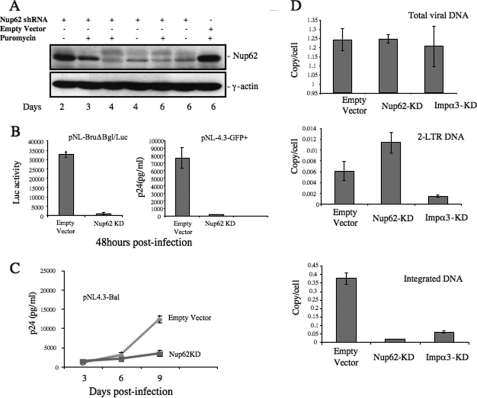
FIGURE 2.
Nup62 knockdown significantly inhibited HIV-1 infection by reducing viral DNA integration. A, C8166 cells were transduced with lentiviral vectors harboring Nup62 shRNA or empty vector and were subsequently analyzed for Nup62 expression by WB at different time points. γ-Actin was included as an internal control. B, inhibitory effect of Nup62-KD on HIV-1 replication in CD4+ C8166 T cells and macrophages. Nup62-KD and empty C8166 cells were infected with VSV-G pseudotyped luc-expressing HIV-1 (pNL-BruΔBgl/Luc) (left panel) or HIV-1 pNL 4.3-GFP (right panel). The Luc activity from cells or HIV Gag-p24 levels of supernatants was measured to monitor viral replication after 48 h. C, monocyte-derived macrophages from healthy donors were transduced with lentiviral vectors encoding Nup62-shRNA and Nup62-siRNA, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” At day 4 post-transduction, MDMs were infected with the pNL4.3-Bal virus strain. Viral replication was monitored by measuring the levels of the HIV-1 Gag-p24 antigen in supernatants at different time points after infection. D, Nup62-KD, importin α3-kDa (Impα3-kDa), and ScRNA-C8166 T cells were infected with HIV-1 pNL4.3 Env+/R−/Luc virus, and 20 h later, DNA was extracted from infected cells, and HIV-1 late reverse transcription products (upper panel), HIV-1 two-LTR circles (middle panel), and the integrated DNA levels (lower panel) were analyzed by RQ-PCR using corresponding primers, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Means and standard errors are representative of the results for duplicate samples from a typical experiment and were confirmed in two other independent experiments.