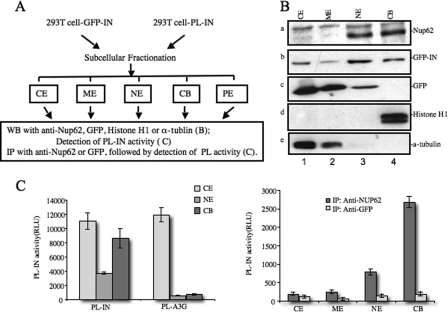
FIGURE 3.
Nup62 binds to chromatin and interacts with HIV-1 IN in both nuclear and chromatin-bound extracts. A, experimental setup. B, subcellular distribution patterns of endogenous Nup62, α-tubulin, and histone H1, and exogenous GFP and GFP-IN were determined by the subcellular fractionation method and WB in 293T cells transfected with the GFP or GFP-IN plasmid. CE, cytoplasmic extracts; ME, membrane extracts; NE, nuclear extracts; CB, chromatin-bound extract. C, 293T cells were transfected with the PL-IN or PL-A3G plasmid for 48 h, fractionated, and then assessed for PL activity (left panel), as described under “Experimental Procedures.” To test Nup62-IN interaction in different fractions, 293T cells were fractionated 48 h after transfection with PL-IN, and each fraction was immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Nup62 or anti-GFP (as the control). The coimmunoprecipitated PL-IN in each fraction was evaluated by measuring PL activity (right panel).